Search ResultsFor "1939"
Disney &Music 28 Dec 2010 09:20 am
Bits and Albert Malette
- This is just a quick reminder to say that The Iron Giant is playing at the Film Forum. Today’s the last day it’ll be screened so get out into the snow and head for the theater.
It was Brad Bird’s first feature. He followed this with The Incredibles and Ratatouille. His next feature will be Mission Impossible 3 (or is it 4?) with another cartoon character,
Tom Cruise.
Showtimes: 1:00, 2:50, 4:40, 6:30, 8:20, 10:10
Oddly, My Iron Giant dvd played wonderfully and had all sorts of extras when I bought it.
I just tried the thing on about four computers and three dvd players, and none of them can read it now. The disc is an expensive piece of garbage at the moment. Thank you WB.
- The Illusionist did well in its first weekend, playing in three theaters – two in NY and one in LA. $16,867 per theater for the weekend. This, on a per screen average, is about twice what the best film is doing and nine times better than Yogi Bear. Of course it’d be lower if it were playing in more theaters, but perhaps this will be an incentive for SONY to get it wider than they plan in January.
- I’m going to start running off more of the Action Analysis notes from the after-hours lectures given at the Disney studio in 1936. To start. let me post this lecture about the relation of music and animation given by Albert Malette, who scored these Disney shorts, among other:
1935 Broken Toys
1935 Cock o’ the Walk
1936 Alpine Climbers
1936 Moving Day 1
1937 Lonesome Ghosts
1937 Little Hiawatha
1938 Ferdinand the Bull
1938 Brave Little Tailor
1938 Moth and the Flame
1939 Ugly Duckling
 1
1(Click any image to enlarge.)
Commentary 20 Nov 2010 09:07 am
Cars 2 / Panda 2 / Signe 1 / Zemeckis 0
- In case you haven’t seen the first trailer for Pixar’s CARS 2, here it is, complete with explosions, Japan, guns, rocket launchers and more explosions. It’s getting to look like Pixar might like doing effects for live-action films. They’re not too far off the mark. The trailer, and no doubt the film, is loud enough to catch somebody’s attention. It should be another winner unless Dreamworks figures out a way to have even louder explosions.
To quote the old SCTV skit: “They blowed him up real good.”
- John Lasseter didn’t have to fire anyone, this time, when he made himself co-director of Cars 2. First time director, Brad Lewis, got himself a partner with Lasseter. I wonder how much time the new co-director will have to spend on the film given all the other chores he’s taken on running both Disney and Pixar. This is old news, but I heven’t talked about this film before.
And you’ve probably seen the trailer for Kung Fu Panda 2 which actually gets my interest, as opposed to the awful Cars 2 trailer. It’s funny. In case you haven’t seen it, here it is.
Lately, one of my favorite blog-spots is Signe Bauman‘s blog. Essentially, this was started to promote a feature she’s trying to get funded, called Rocks In My Pockets. She writes once or twice a week, and each of her pieces is so personal and informative that I can’t help but getting enveloped in what she has to say. She has a good seven part series on fundraising for a film, especially when the film is not very commercial. She writes about the difficulty of accepting rejection when you’ve applied for a grant and don’t get it. She’s even written about Depression. Check out the site and go back a bit to read her commentary. Very interesting stuff.
- When the story of Robert Zemeckis having been approached to remake The Wizard of Oz from the original 1939 script hit the blogs, everything went wacko. Lots of rumors flew like monkeys in the sky.
Well the truth is that Zemeckis turned down the job when discussing it with WB. Of course, this doesn’t mean the film won’t get remade; it just means that the #1 Motion Capture guy isn’t planning to do it until he can tear apart The Yellow Submarine. That, of course, will be his next opus – due out in 2012. Maybe entering it in the Oscars, that year, will give us 16 entries.
Speaking of which, I notice that there are only 15 accepted feature documentaries for the Oscar. Somehow, they’ll still have five nominees, while animation – with the same 15 acceptable number – will only be allowed 3 nominees. Something smells rotten in Hollywood.
- Today I’ll be out all day screening the animated shorts which were deemed eligible for Oscar consideration. That should take about 5½ to 7 hours of watching shorts. It’s grueling, but I love doing it. I see that Cartoon Brew has listed the shorts that’ll be screened. Two years ago I listed the shorts and was chastised by the Academy in a very formal letter. The following year, they started listing the titles. So I like to think that I pushed them into realizing that the shorts could be treated no differently than the features, and they could be announced to the public without hurting their chances. (It gives a little more publicity to the shorts filmmakers, and they’re the ones who could use it.)
Animation &Articles on Animation &Disney 22 Oct 2010 07:46 am
Oskar Fischinger at Disney
The following article appeared in the 1977 Anmation Issue of MILLIMETER MAGAZINE as edited by John Canemaker. (Some of those commercial magazines were just excellent back then, and we never seemed to notice or properly appreciate them.)
or, Oskar in the Mousetrap
by William Moritz
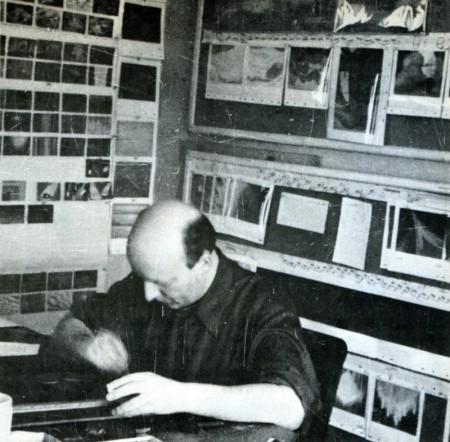

Oskar Fischinger at work at the Walt Disney Studio in 1939
Courtesy of Mrs. Elfriede Fischinger, all rights reserved
The official Disney account of the origin and making of FANTASIA has been told many times — from the early press releases, programs, and Feild’s wide-eyed, idolatrous book from 1942, THE ART OF WALT DISNEY (all united by the “official studio policy”/ mannerism of discussing primarily Walt Disney himself as if he had conceived and designed the films almost single-handedly), down to the more reasonable, carefully-researched materials published recently, such as the article by Disney archivist David R. Smith for MILLIMETER’S 1976 animation issue, and Bob Thomas’ new biography, WALT DISNEY, AN AMERICAN ORIGINAL.
I have already given an outline of another side to this story in my bio-filmo-graphy of Oskar Fischinger (FILM CULTURE 58-59-60-, 1974, pp. 61-65), but Fischinger’s tale bears re-telling since clearly a full understanding of the matter lies in discovering all that went on behind the scenes and in Fischinger’s heart-of-hearts.
Oskar Fischinger, who was a year older than Walt Disney, devoted his major energies throughout his life to abstract animation. In the early Twenties, while the Disney brothers assembled Ub Iwerks and a remarkable collection of talents to form an animation studio for production of Alice and Oswald cartoons, Fischinger, working on his own, struggled with radical experiments in non-objective imagery — from sliced wax to multiple-projector light shows. Even before sound film became available, Fischinger synchronized his abstract films to phonograph records and live musical accompaniments, because he found that the analogy with music (i.e., abstract noise well-developed and widely-accepted non-objective art form) helped audiences to grasp and accept the nature and meaning of his “universal”, absolute imagery. Oskar never meant to illustrate music, and often screened his “sound” films silently for already sympathetic audiences.
At the same time Iwerks/Disney’s Mickey Mouse and SILLY SYMPHONIES (and clever mass-marketing techniques) began to gain world-wide acclaim for the Disney Studios, Fischinger also enjoyed a moderate international renown as well, with his black-and-white STUDIES playing as novelty shorts with features from Uruguay to Japan. And while Disney began to win Academy Awards for his shorts, Fischinger also won grand prizes at film festivals in Brussels and Venice.
By 1935, Fischinger had made at least 35 abstract animated shorts, and stated as his New Year’s wish in the Berlin trade paper FILM KURIER that he wanted most to create an animated feature composed entirely of non-objective imagery and diverse music (he had used jazz, toyed with experimental electronic music and his own synthetic drawn soundtracks as well as classical music).
A scene from Walt Disney’s FANTASIA (1940)
Unfortunately for Fischinger, political events militated against him for much of his life, but he still produced a body of work that plays increasingly in theatres and museums as several full-evening programs.
The Nazi government had banned abstract art as degenerate, and was officially outraged that Fischinger’s COMPOSITION IN BLUE won festival prizes. Oskar in turn happily accepted a contract with Paramount and sailed for Hollywood in February, 1936, never to return to Germany. Unfortunately he spoke no English and encountered tremendous, frustrating difficulties in his early studio jobs. He assumed Paramount wanted him to pursue the style of his prize-winning COMPOSITION IN BLUE, but instead they wanted more representation and cuter work like his Muratti cigarette commercials. After he had completely painted and photographed a color abstract sequence (later called ALLEGRETTO), the director Mitchell Leisen insisted the piece be re-done in black-and-white with representational images of musical instruments and other pop trick effects overlayed. The resulting studio version disgusted Fischinger and he quit Paramount only half-a-year after he started there.
His second American film, AN OPTICAL POEM, made for MGM under William Dieterle’s aegis, proved one of Oskar’s finest works, and though not exactly a box-office sensation, played prestige bookings with first-run features, and was mentioned by one critic as a likely Oscar nominee (which caused Fischinger to quip, “Why bother giving me Oscar? I am Oskar!”).
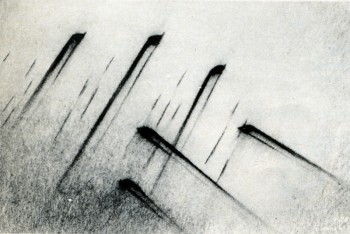
A Fischinger pencil sketch (with numerical
motion-phase breakdowns) for “Toccata and
Fugue” section of Disney’s FANTASIA.
After his MGM option was not picked up, Fischinger drove to Detroit and New York seeking backing for a feature-length animated film based on Dvorak’s “NEW WORLD” SYMPHONY, which he hoped to be able to present at the World’s Fair. Although this project never materialized, Oskar dallied in New York because he discovered a new ambiance there: unlike Hollywood, he was treated as a major artist in New York, invited to screen his films and exhibit paintings, dine with leading filmmakers, critics and painters, spend weekends at the country estate of Guggenheim Foundation curator Hilla Rebay. He returned to Hollywood only when his agent cabled that he had a job for him at Disney.
What a rude shock Fischinger received upon his return! Already in Berlin, Oskar had been attracted to Leopold Stokow-ski’s grand orchestral arrangements of Bach and had tried to get music rights to some of his pieces. When Fischinger found that Stokowski was his co-worker at Paramount, he once again proposed a series of shorts or an anthology feature. Stokowski was initially quite receptive and wrote Fischinger (October 9, 1936, on Paramount stationery), “I should be very happy if we could work together — you doing what is seen, I doing what is heard.” And he received from Fischinger such elaborate ideas as (November 15, 1936, in German):
“If you are here at Christmas, I’d like to make a full-length shot of you in such a way that the visual part of the film could begin with you conducting the first few bars of the music, and then the eyes of the viewer would glide with a movement of your hands off into endless space where the rest of the visuals would unfold. ”
Nevertheless, after several conferences, Stokowski decided that the project would be too expensive and complex for Oskar to animate alone, and suggested that they seek support from a major studio, perhaps Disney. Fischinger held little hope for satisfactory help from Hollywood, especially after his experiences, and furthermore he knew from gossip that Disney, despite his successes, was under severe strain, borrowed and mortgaged to the hilt. And Oskar’s worst fears were seemingly confirmed when he returned to Hollywood in November, 1938, to find that while Stokowski was being honored as Disney’s major collaborator on “The Concert Feature”, Fischinger was being hired for $60-per-week (Paramount had paid him $250) as a “Motion picture cartoon effects animator”.
Fischinger accepted the job since work was scarce and he had four children to support, but for him the Disney episode proved a nightmare which so angered him that he conspicuously avoided talking about it in later years. Only once did he write a note on his Disney adventure (in a letter to a friend), and it expressed well his chagrin:
“I worked on this film for nine months; then through some “behind the back” talks and intrigue (something very big at the Disney Studios) I was demoted to an entirely different department, and three months later I left Disney again, agreeing to call off the contract. The film “Toccata and Fugue by Bach” is really not my work, though my work may be present at some points; rather it is the most inartistic product of a factory. Many people worked on it, and whenever I put out an idea or suggestion for this film, it was immediately cut to pieces and killed, or often it took two, three or more months until a suggestion took hold in the minds of some people connected with it who had their say. One thing I definitely found out: that no true work of art can be made with that procedure used in the Disney Studio.”
At first, Fischinger threw himself whole-heartedly and good-naturedly into the project. He gave prints of his films to be screened weekly for the entire Disney staff, so his influence was pervasive (spilling over onto other films like DUMBO, the South American films, and PINOCCHIO, for which Oskar actually animated the magic wand of the Blue Fairy). In the mimeographed transcript of the story meeting for February 28, 1939, Walt Disney says (p. 1): “Everything that has been done in the past on this kind of stuff has been cubes, and different shapes moving around to the music. It has been fascinating. From the experience we have had here with our crowd — they went crazy about it. If we can go a little further here and get some clever designs, the thing will be a great hit. I would like to see it sort of near-abstract, as they call it — not pure. And new.”
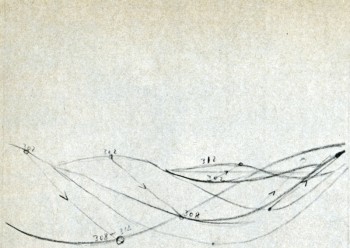
Fischinger’s numerical motion-phase breakdown
for “the Wave” scene in “Toccata and Fugue”
section of FANTASIA.
© Fischinger Trust, all rights reserved.
Perhaps because of the uneasy proximity of Fischinger, Walt exhibits a certain suspiciousness about abstraction, accompanied by a rather defensive attitude towards the prospective audience.
January 24, 1939, p. 2:
Walt Disney: You should give something that the audience will recognize. I don’t think the average audience will fully appreciate the abstract; but I may all be wrong —
Stokowski: Yes, they may be way ahead of us.
or, January 24, 1939, p. 7:
Walt Disney: What will Bach lovers think of this?
Stokowski: They will be against it, I think; but the public will love it.
Walt Disney: Well, the general idea here looks good to me. I only wonder if we’re going a little too gypsy in the color—
or, February 28, 1939, p. 5:
Walt Disney: If we can get a little connection behind this, the public will take to it. It would be better than some wild abstraction that you can’t get anything out of at all. Right there is where the music sounds most like an organ, so the public decides it represents an organ.
or, February 28, 1939, p. 8:
Walt Disney: Do you think we ought to have pictures in mind through this thing? Then we won’t get a conglomerate mess — an abstraction.
or, JuneS, 1939, p. 1:
Walt Disney: There’s a theory I go on that an audience is always thrilled with something new, but fire too many new things at them and they become restless.

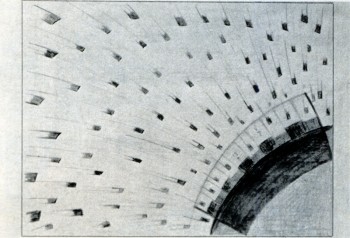
The “wave” scene as it appears in FANTASIA.
©Walt Disney Productions.
Fischinger’s assertions about the unhealthy competitive committee work at Disney would seem to be borne out by the conference notes in which we see during nine month’s of work on the “story” incredible floundering, dreary discussions and re-discussions of each scene, groping and pushing without any controlling factor besides making an entertaining film.
Because he knew little English, Fischinger never spoke up during these story conferences (neither did Kay Nielsen), and further became the butt of endless practical jokes on the part of his jealous co-workers. Some fun-loving boys of the Disney staff, unwilling to deal maturely with the plight of a refugee artist, pinned a swastika on Oskar’s office door September 1, 1939, the day the Nazi armies invaded Poland. Fischinger applied for a release from his contract and after two months of red tape, terminated his employment at Disney, October 31, 1939, Halloween.
Fischinger kept about 100 of his sketches and drawings for the Bach “Fugue”, including some lovely pastels showing melting meanders and supple lozenges much as they appear in the final FANTASIA, as well as half-a-dozen beautiful images that were probably never realized on film. The most extensive unit involves twelve poster-color and 60 pencil drawings (with numerical motion-phase breakdowns) that detail the sequence in which alternating left-and-right-hand “waves” surge toward the viewer. While this turned out to be one of the more impressive moments in the Disney film, a comparison with Oskar’s original sketches shows how much more powerful, subtle and imaginative the sequence might have been if Fischinger’s intentions had been honored — with his choice of monochromatic turquoise and celadon hues for the (somewhat flatter) wave motion overlayed with scintillating geometric figures in browns, Chinese red, and graduated yellow/oranges, all of the elements flowing cogently and vigorously out of each other, as opposed to the simplified Disney image of fat, melon-ribbed waves slightly off-balance in shades of flagrant purple distractingly at constrast in “realism” to the (needlessly) clouded sky behind. All in all, the Disney version of the “Fugue” seems painfully close to the Paramount adulteration of ALLEGRETTO.
Much of Fischinger’s work seems entirely lost. After looking at some of Oskar’s sketches (August 21, 1939, p. 3), Walt Disney comments, “I think the contrast of black and white, and then a little color coming in, would stand out. ” but I don’t think such an effect reached the final version of FANTASIA. Evidently some of Fischinger’s own animation was filmed at least in the pencil test stage, since after viewing some material on a moviola Disney comments (August 21, 1939, p. 7) “Oskarhas a pulsing effect in his test.”
To me, Disney was actually the loser in the matter. Each year Fischinger’s genius and the sincere consistencly of his films becomes more widely acknowledged, while every year the moments of unbearable kitsch, lapses of taste, questionable values, and hodge-podge of stylistics that mar most of the Disney Studio product are becoming more obvious to everyone. For all its considerable virtues of self-parody, rich color and design, etc., FANTASIA falls easily victim to its own shortsightedness so that the burlesque of Bozetto’s ALLEGRO NON TROPPO carries devastating bite.
At least Fischinger had a few of the last laughs in the matter. After leaving the Disney Studios, he devised a set of seven superb collages, among his most charming and highly prized works, showing Mickey and Minnie Mouse (cut from comic books) “reacting” to reproductions of abstract paintings by Kandinsky and Bauer (cut from a 1938 Guggenheim Museum catalogue). And years later, when Disney made the documentary TOMORROW THE MOON, they inadvertantly honored Oskar by using a clip of his pioneer special effects of the rocket launching from Fritz Lang’s FRAU IM MOND, made a quarter of a century earlier.
Books &Commentary &Disney &Story & Storyboards 02 Aug 2010 10:08 pm
Joe and Joe
- Today is the day that John Canemaker‘s book, Two Guys Named Joe: Master Animation Storytellers Joe Grant and Joe Ranft officially hits the stores. I urge you to take a look and go for it. The book is great.
 - It was about nine months ago that John Canemaker let me read the galleys of his new book, Two Guys Named Joe: Master Animation Storytellers Joe Grant and Joe Ranft. I’d been aware of the book for a couple of years now, and whenever I’d heard John talk about it I wondered how the two guys fit in together to make a book. When I was handed the galleys, I moved slowly ahead with some trepidition.
- It was about nine months ago that John Canemaker let me read the galleys of his new book, Two Guys Named Joe: Master Animation Storytellers Joe Grant and Joe Ranft. I’d been aware of the book for a couple of years now, and whenever I’d heard John talk about it I wondered how the two guys fit in together to make a book. When I was handed the galleys, I moved slowly ahead with some trepidition.
I basically knew who the two Joes were from my reading and my NY attempts to keep up with the Hollywood system. Joe Grant was an old timer who’d dominated the Disney modelling department (the only time there was a department exclusively for model sheets), and he’d come back to act as one of the wizened artists helping to shape the new “Renaissance” in the animation community. Joe Ranft was one of the key CalArts guys who’d gone through the Disney system on his way to Pixar where he helped to shape that studio. There’s no doubt he was key to Toy Story, A Bugs Life and Monsters Inc.
What connection would John Canemaker have for tying these two together? Would that connection be enough to fill a book?
Of course, all such conjecture was stupid on my part. The book, as it turned out, is one of John Canemaker‘s finest, and that’s saying a lot. John, after all, is one of the best of our animation historians. His material is well researched, his facts are accurate, and his information is always pertinent and absorbing. He is also a good writer. He tells a story and reveals his information as any good writer would. There’s a solid construction to all of his books, and he lets you into the book in a comfortably relaxed way so that you’re absorbing the story and facts all together, and you are pulled into the book. This is the greatness of Two Guys Named Joe.
As for the connection, John explains that well. Not only, of course, within the book, but he had this succinct statement to make in an interview with Amid Amidi: “I saw the possibility of an overview of the history of storytelling at Disney and Pixar through a very human story of two artists straddling the 20th and 21st centuries.” And that’s exactly what John uses the book to do. He wants to really upchuck the earth of the story departments of both Pixar and Disney, and he does a good job of it.
I’ve now read the book twice. Once in galley form, once in final book form. The book is a rich-looking item full of the finest artwork from storyboards, printed material and developmental art. It’s a gorgeous book.
However, the real gold is in some of the writing and treasured bits that John has dug up to support his material. Here, for example is a small piece about Alice In Wonderland’s story development:
 A March 15, 1939, story conference transcript reveals Walt’s frustration with the project:
A March 15, 1939, story conference transcript reveals Walt’s frustration with the project:WALT: (To Joe) Have you been through A//ce in Wonderland lately?
JOE: No. I’ve been through the script though. I think there are some pretty good situations in this.
WALT: Yes, and some, too, that are not so good.
JOE: I like the stuff on the disappearing cat—swell possibilities in that.
WALT: Yes. Let’s see. What are the good situations?
JOE: The tea party stuff is good.
WALT: Yes, the tea party is to me the best. . . You
know, I think we’re missing a hell of a lot in the stuff that is our medium. . . everything isn’t dialogue. Talk, dialogue business that depends on dialogue, hinges on dialogue.
Disney then tore into an unfortunate writer named Dana Coty.
WALT: I’m saying that to you because I think maybe
you’re the one that’s responsible for a lot of silly business that has no basis on anything funny.
DANA: Well, in the duchess’s house, I wrote that very loosely to begin with, Walt.
WALT: I don’t give a damn how you wrote it. It’s what we’re driving at. If it hasn’t got a basis for something funny, don’t write it! There’s no use writing the thing and then alibi-ing for it afterwards. It just throws us off the, track. Don’t just write anything to fill up some pages. We had the same criticism, the last time we were together.
John uses this anecdote to not only say something about Disney, himself, but the way he communicated with Grant and the hostility he might display for others. He did not mince words or waste time where he thought it was wasted. They were trying to solve the problms they saw in Alice In Wonderland, but we learn that Grant, Huemer and others felt that Disney was the problem. They felt he didn’t quite understand the Victorian humor of the original and tried to gag it all up. It’s just one wonderful excerpt dug deep in the book.
Another gem of a sequence involves Joe Ranft. It’s the point just when the Pixar artists are trying to sell Toy Story to the Execs at Disney. They’re doing everything in their power to make the film story good while placating the Disney people, and they’re having a hard time of it.
- Disney insisted the production move to Los Angeles so the studio could oversee things. “And give us more notes,” Ranft lamented.
Lasseter, whose “heart was broken,” begged for a two-week reprieve to turn things around. After obtaining Disney’s skeptical permission, Lasseter, Ranft, Docter, and Stanton resolved to “make the movie we want to make!”
. . .
The process included writing, gathering more material, constant meetings, weeding out, refocusing, and . . . more meetings. “Two or five heads are better than one,” Ranft believed. “If you can work together without killing each other, you an accomplish a lot.”
Going forward, Pixar gladly accepted notes from Disney and welcomed participating in brainstorming sessions with their artists. “But,” Ranft said, “we’d go away and really think about [the notes]. A lot of times we’d go, ‘No. Here’s the real problem!’ And it was even deeper than the notes. ‘And here’s how we’re going to fix it.’”
Regarding the creative process, Ranft once said, “It’s a challenge. The final product is the goal you’re searching for. [Your little sequence is] gonna get smashed, trashed. It’s gonna come apart for the good of the final film . . . it’s a paradox. You’ve got to put yourself into it, and then you’ve got to take yourself out of it. Be objective and not be hurt.”
And that’s the point of the two guys. They understood the value of the story and the center of the films they worked on and over. Nothing mattered, including personal insult, as long as the story came out right. They were film artists and knew how to get what they needed to complete their goals.
My personal preference is to want to know more about the old timer and to learn more about the golden age. However, it’s totally my bias, and the proof of this book’s success is that I was completely absorbed by all that was written about both men.
This is more than a good book. Anyone in love with animation should own a copy and read it carefully. There’s a lot there, and it’s all good. It’s stunningly designed with beautiful animation art treasures well displayed.

A telling board by Ranft.
________________
Amid Amidi offers an excellent interview with John Canemaker on the subjects of the book at his Cartoon Brew site. I recommend you all read it.
There’s also a video promo you can catch on YouTube if you’re more visually oriented.
Articles on Animation &Independent Animation 18 Jun 2010 07:42 am
Norman McLaren – WHO ?
- I was recently in a conversation with a young animation student. In the course of our chat, the student commented on a DVD on my desk; he didn’t recognize the filmmaker’s name. Norman McClaren. I gave him a small lecture about the master’s work and suggested the student start doing some research (even if only on YouTube.)
I came across this article by Gerald Buddner in “The Art of the Animated Image”, and anthology edited by Charles Solormon and published by AFI in 1987. I have to post it.
at Work
First Impressions of Norman McLaren
BY GERALD BUDNER
ver 40 years ago—the summer of 1946—while visiting a school friend who had a summer job at The National Film Board of Canada, I was invited to Miss Evelyn Lambart’s dinner party for Norman McLaren. Conversation was marvelous, dinner was delicious and helpings very ample. I remember it included the perfect fruit dessert—this was followed by another, a “shape.” This Victorian Triumph about 14″ high of molded Creme de Menthe was, sad to say, more than any of the guests could manage, which caused but a moment of disappointment. Suddenly Norman lifted Miss Lambart’s beautiful Georgian dessert trowel, and in about a minute flat, with a few deft strokes, was able to convert the quivering delight into a sculpted Jade Chinoiserie in a Brighton pavilion style—complete with grottoes and waterfall, bridge with fisherman catching giant carp, a pagoda above a lily pool complete with wading storks. The whole exercise was super speedy and enchanted the assembled company. From that moment, I knew I was privileged to be in the presence of a Genius.
The following morning at the Animation Department in the abandoned sawmill, I was invited to see the artists – at work.
Thinking I would witness leaping figures, etc. I was instead spellbound to hear a few absolutely clear and fresh phrases of Bach, drawn—that’s rightdrawn on the sound track. This was the beginning of a 40-year-long enchantment. The magic of the shy McLaren was at work.
From the beginning, the professional life of Norman McLaren was characterized by a creative spirit toward art and music, a finely honed perception for the importance of technical brilliance, a unique sense of humor and a deeply developed sympathy for the whole of mankind. Frugal by nature, he was accustomed to working with the scantiest of means. Inspired by movement, he was able to use characters and even props as puppets. He scratched sprightly images with needles and razors onto raw film stock with delightful and unexpected effects. One of the first animators to experiment with drawing, scratching and engraving both the picture and sound directly onto film, he is also acknowledged as being one of the pioneers of 3-D animation. The effects of his innovation grow more impressive with each successive viewing of the films. Meanwhile he drew and painted continually, offering his works to his admiring friends.
Born in Stirling, Scotland in 1914 to an artistic and cultivated family, he was encouraged to pursue music and art from a very early age. He began a five year course at the Glasgow School of Art, headed by John Rennie Macintosh, specializing in interior design which related to the family business. He was already intrigued with film, and at twenty years of age, he entered two films in a Scottish amateur film festival, where they won awards and attracted the attention of the adjudicator, John Grierson.
Impressed by the obvious talent of the young artist, he offered McLaren a position in London with the prestigious General Post Office film unit where he was taught the craft of film-making. After leaving the G.P.O., he worked as a cameraman during the civil war in Spain. Haunted by his nightmarish experiences, he came to New York in 1939 where he was encouraged by the founders of The Guggenheim Museum and other New York film people.

Begone Dull Care, 1949, McLaren at work with Evelyn Lambert.
At that time, the Canadian government created The National Film Board with John Grierson as the first Government Film Commissioner. The “Board” had a very significant mandate to fulfill, not the least part of which was to help, through the film medium, to unify a diverse, thinly populated and vast country. Grierson was quite up to this task, but was soon aware of the danger posed by the very serious and worthy, but nonetheless somewhat heavy-handed zeal of the young filmmakers. This heaviness, although well intentioned, could have been disastrous for a new and untried governmental film organization. By 1941, Grierson was able to convince McLaren to bring his inventive genius, his wacky humor and his artistic conscience to Ottawa, to add some leaven to the earnest mass of vital information being produced for a country at war.
The wisdom of this action was soon evident: the meteoric power of the amazing McLaren was launched. The National Film Board would never be the same! Canada would never be the same! The results would bring delight to Canadian filmgoers and to people around the world, fame to McLaren, and honor and prestige to his chosen country.
In the first years at the “Board,” McLaren was encouraged to establish an animation studio, which attracted other young talents who would contribute richly to the art of animated film in Canada. Evelyn Lambart, George Dunning, Jim McKay, Rene Jodoin, Colin Low, Grant Munro and many others soon joined him. The technical excellence and the level of artistic accomplishment achieved by McLaren’s studio soon attracted the attention of film people across Canada and in other countries. They scorned cheap commercial effects, which were a dangerous trap in this very exploitable medium. Their films were recognized as having something very special to say in a very special way. In Britain, France and The United States this plateau of achievement and artistic integrity was a cause for wonder; the choice of subjects, the graphic styles and the technical skills combined to lift animation to the plane of ART. McLaren produced many wonderful films in this early period.
In 1949, UNESCO invited McLaren to visit China and teach Chinese artists and educators audio-visual techniques. He found the experience was very rewarding on the humanitarian side, as the impoverished Chinese were at war and desperately anxious to use the simplest resources to educate their gigantic population.
This profound experience of war and revolution left an indelible mark on his sensitive and impressionable nature, as well as on his physical health.
On his return to Canada in 1950, he was invited to create films in 3 dimensions for the Festival of Britain. Around is Around and Now is the Time are the result, considered by many to be classics of this technique both for the impact of their fabulous imagery and their unprecedented and powerful sound tracks. Although rarely seen today, the films are regarded as precursors of most 3-D animated films.

Neighbors, 1952.
It was not surprising that an anti-war film soon occupied him, and in 1952 Neighbors captured the imagination of the film world. The next year it won the Academy Award for best documentary short, as well as numerous other prestigious awards in Canada, the United States and Italy. The technique he employed animated both figures and props, which he christened PIXILLATION. The picture of escalating violent battles for possession of a single flower still sings out his sentiments on the subject of war.
Rhythmetic is a very engaging game-like film made with Evelyn Lambart. Quite surprisingly it enjoys an unexpected revival today, since young people equate it with the computer a surprising example of deja vu in a film made in 1956. Lines Vertical was also made with Evelyn Lambart, in I960. The lines were engraved on black film stock with a stylus. McLaren later told me that he was inspired to make his next film Lines Horizontal having observed the telegraph wires “animate” through the train window while travelling between Ottawa and Montreal. He used his earlier Lines Vertical to create a new film by turning the images 90 degrees! Very frugal indeed.
Mosaic (1965) combined the two Lines films by printing them together and featured a sound track he engraved himself. Pas de Deux. (1967) uses ballet dancers. The stroboscopic effect of slowed movement and controlled back lighting offers sculptral dimensions of magical proportions and depth. The sensual visual effect celebrate his passion for movement in a most elegant way—to me reminiscent of classical bas reliefs brought to life with amazing refinement. These themes were expanded in 1972 where the movement was further slowed down and the emotional impact expanded in Ballet Adagio.
All McLaren’s experiments in animated sound came together in Synchromy made in 1971. The visuals are actually identical with the sound, which was accomplished by photographing the sound cards he had made years earlier. These patterns comprise both the optically colored visuals and the sound track.
To celebrate the accomplishments of his two Parisian animator friends, American Claire Parker and Russian-born Alexandre Alexieff, McLaren made an erudite film Pin Screen in 1973. The velvety light and dark effects made with their sophisticated invention offer the effect of metamorphosing chiaroscuro, resembling stipple engravings of incredible softness and tenderness.
Following this, McLaren and his long-time associate Grant Munro created a series of films for educational use, which elucidate the basic principles of movement in a clear and easily comprehensible way. Animated Motion numbers one, two, three, four and five are very useful for students of animation, and should serve as a springboard for young artists.
Narcissus represents the peak of films that exploit optical effects. In his own words “During the first part of the film Narcissus no special effects were employed, but from the moment Narcissus sees his own image in the pool until the end of the film a whole variety of optical effects were used. Narcissus’ image when flipped left to right and upside down, was made to go in and out of step with itself by freeze-framing, double framing and skip framing. At times in the original shooting Narcissus had to perform two opposing roles which were later optically combined in the same frame. In one such sequence, various flicker effects were introduced, in another more extended sequence the movements (motives or actions) of each ‘Narcissus’ by a very complex optical technique are turned into flowing blurs.” Norman ’81.

McLaren in retirement.
In the last film made with and about him in 1983 for a festival of animation films in Holland, he underlined how grateful he was for forty-two years of artistic freedom enjoyed at The National Film Board of Canada. All share gratitude for freedom, for we enjoy it too. I am confident that millions will continue to be grateful for a very long time to come. The number of his films long and short totals sixty. From the words of his life-long campanion Guy Glover, written as a foreword for a monograph published by The National Film Board “McLaren – 1980,” let me long and short totals sixty. From the words of his life-long campanion Guy Glover, written as a foreword for a monograph published by The National Film Board “McLaren – 1980,” let me quote:
“Far from the Talking Picture -That vast province of the Cinema that borders,
indeed overlaps, on the Realm of language -
There exists yet another province of the Cinema
where talk is limited and which touches on the frontiers
of Music and Dance. In a corner of that province is to be found
the little garden of Norman McLaren whose films talk only through image and movement.
A birds-eye view of McLaren his life and film work has been attempted,
without forgetting, of course,
that it is in the films themselves
that his creative character is most clearly expressed.”
Animation Artifacts &Books &Disney 26 Feb 2010 08:42 am
El Sastrecillo Valiente
Ignacio Carlos Ochoa is an animator in Argentina. (Check out his site; his work is extremely good.) He recently wrote to tell me that he found a book at his mother’s house – El Sastrecillo Valiente/The Brave Little Tailor. (Oddly enough, I had just begun scanning the Frank Thomas scene from this film that started posting last Monday.)
Ignacio sent scans of the book, and it appears to be the Spanish edition of the Whitman book, originally published in English in 1939. He guessses this edition to date from the 50′s and published by PEUSER LTD. (“On the back cover is writed ‘Peuser Ltd.’ in a very small size.”) At the first page we can read that the book was printed by “LibrerÃa Hachette” .
I’m grateful to Iganacio for sending these great scans, and I hope you like the book:

(Click any image to enlarge.)
Articles on Animation &Hubley 25 Feb 2010 06:40 am
Finian’s Rainbow – alt
Yesterday I posted this very same article by giving the PRINT Magazine layout. Today I offer an alternate version, since I think it’s an important piece, wherein the text would be html and the illustrations could be posted larger. Hence, I’ve decided to post it twice, for whatever that’s worth. At least it allows me to keep it running for second day.
.
.
by John Canemaker
Animation innovator, John Hubley was slated to design and direct a film version of the Broadway hit, Finian’s Rainbow. But this was the fearful 50s and the witch-hunting zeal fo the time doomed the project. All that remains are 400 storyboard sketches which recently surfaced and are sampled here.
.
 On January 10, 1947, the musical Finian’s Rainbow opened on Broadway to rave reviews, precipitating a successful run of 725 performances. In the fall of that same year, the U.S. Congress-approved House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) began a long-running show of its own: the official sanctioning of an “Inquiry into Hollywood Communism.”
On January 10, 1947, the musical Finian’s Rainbow opened on Broadway to rave reviews, precipitating a successful run of 725 performances. In the fall of that same year, the U.S. Congress-approved House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) began a long-running show of its own: the official sanctioning of an “Inquiry into Hollywood Communism.”
Amid the wreckage of lives and careers cut short during a decade of insidious HUAC-inspired fear and persecution were numerous film and TV projects fated never to see completion, including a feature-length animated cartoon version of Broadway’s Finian’s Rainbow.
Information about this intriguing production (abruptly halted in February 1955) has been scant; in Euclid tiled Drawings: The History of Animation (Knopf, New York, 1989), Charles Solomon mentions Finian’s as part of the career of John Hubley, the project’s director/designer: “Some animators believe Hubley’s politics were the source of many of the problems that surrounded his ill-fated effort to make an animated feature based on the
Gregorio Prestopino (L) one of ___ musical Finian’s Rainbow.”
many art directors who worked
on the animated Finian’s Rainbow
talks with John & Faith Hubley
Within the animation industry, there have been rumors of an inspired Hubley-designed color storyboard (alleged to be lost), and of a “dream” soundtrack recording (never publicly released), featuring a stellar cast that included Frank Sinatra, Ella Fitzgerald, Louis Armstrong, Oscar Peterson, Barry Fitzgerald, Jim Backus, David Burns, and two stars from the original Broadway cast, David Wayne and Ella Logan.
Recently, over 400 sketches from the Finian’s storyboard surfaced after nearly four decades of careful storage by Fred J. Schwartz, president of the film’s financing company; in this issue, PRINT is publishing examples of artwork from the animated Finian’s Rainbow for the first time ever. Interviews with Schwartz and other survivors of the project led this writer to a copy of the director’s original script and a reel of the now-legendary soundtrack recording. A detailed history of the “lost” film follows, making it possible to conclude that Finian’s Rainbow would have been an important con-tibution to the history of animated features, opening up the Disney-dominated, child-oriented genre to new sophistication in content and design.

A sequence of color story continuity sketches by John Hubley for the
musical number “Something Sorta Grandish” sung by the love-struck
leprachaun Og as he dances with anthropomorphic laundry.
Animation was the medium chosen to bring Finian’s Rainbow to the screen simply because Hollywood’s live-action studios were reluctant to take on the property. (Eventually, in 1968, Fred Astaire starred in a leaden live-action film version directed by Francis Ford Coppola.) “The motion picture industry refused to make a movie of this smash musical because of its story content,” says Michael Shore, the entrepreneur who started the ball rolling toward an animated production in 1953. The show’s composer, Burton Lane, agrees: “The studios were a little fearful of the subject of racial discrimination.”
.
 Finian’s Rainbow begins in Ireland, where wily old Finian McLonergan steals a pot of gold from the leprechaun Og. Finian travels with his daughter, Sharon, to America’s Rainbow Valley, a rundown tobacco plantation near Fort Knox, worked by black sharecroppers, where Finian believes the “peculiar nature of the soil lends an additional magi cal quality to gold.” He leases a parcel of land to bury the gold from Woody Mahoney and his sister, Susan the Silent, who dances to communicate (“foot-talkin”‘). Woody and Sharon fall in love. The tiny land parcel is also coveted by Judge Rawkins, a wealthy Southern bigot (“My family’s been having trouble with immigrants ever since we came to this country!”), who goes ballistic when a geologist discovers “an amazing concentration of gold” on the property. In the meantime, the leprechaun Og, who followed Finian to Rainbow Valley, is slowly becoming mortal as a punishment for losing the gold; he helplessly falls in love with both Sharon and Susan. Judge Rawkins attempts to dispossess Finian with a ___A color character model of
Finian’s Rainbow begins in Ireland, where wily old Finian McLonergan steals a pot of gold from the leprechaun Og. Finian travels with his daughter, Sharon, to America’s Rainbow Valley, a rundown tobacco plantation near Fort Knox, worked by black sharecroppers, where Finian believes the “peculiar nature of the soil lends an additional magi cal quality to gold.” He leases a parcel of land to bury the gold from Woody Mahoney and his sister, Susan the Silent, who dances to communicate (“foot-talkin”‘). Woody and Sharon fall in love. The tiny land parcel is also coveted by Judge Rawkins, a wealthy Southern bigot (“My family’s been having trouble with immigrants ever since we came to this country!”), who goes ballistic when a geologist discovers “an amazing concentration of gold” on the property. In the meantime, the leprechaun Og, who followed Finian to Rainbow Valley, is slowly becoming mortal as a punishment for losing the gold; he helplessly falls in love with both Sharon and Susan. Judge Rawkins attempts to dispossess Finian with a ___A color character model of
phony writ condemning the sharecroppers’ dwellings; but ____“himself,” Finian McLonergan,
when Sharon wishes (inadvertently over the magic gold) that_the film’s protagonist who was
Rawkins was in the sharecroppers’ shoes, his skin promptly __voiced by Barry Fitzgerald.
turns black.
The reviews for the Broadway production lavishly praised the performers, Michael Kidd’s choreography, the sets and lighting by Jo Mielziner, Burton Lane’s music, and E. Y. (Yip) Harburg’s lyrics (the show’s hit songs include “Old Devil Moon,” “How Are Things in Glocca Morra?,” “Look to the Rainbow,” and “If This Isn’t Love”), but they were less glowing about the book, which some critics faulted as an uneasy mix of fantasy and reality.
“Among other things,” wrote Richard Watts, Jr., in the New York Post, “Finian’s Rainbow is equipped with what may well be the most elaborate plot since War and Peace. Taking in its stride handsomely diversified elements from pseudo-Irish mythology, complete with an oversized leprechaun and a mystic pot of gold, to left-wing social criticism, embracing sharecroppers, the poll tax, anti-Negro senators, atomic energy, the gold at Fort Knox, the Tennessee Valley Authority, and the economic future of mankind, the book mingles the authors’ imagination with their politics amid much abandon…. If some of the political comment were just a little less blatant, the plot just a bit more inventive… the tale of the leprechaun’s mission to America would have been even happier.” Brooks Atkinson of the New York Times found the “stubborn shot-gun marriage of fairy-story and social significance… not altogether happy. The capriciousness of the invention does not last throughout the evening.”

Exquisite charcoal story-continuity sketches, delicately rendered
by John Hubley, depict a sequence of moonlit magic wherein Finian
buries the stolen crock of gold – on which the plot of Finian’s Rainbow
hinges – and is confronted by Og. The voice of Og was supplied by David Wayne,
who originate the role in the Broadway production.
.
“It’s heavy-handed,” says Michael Shore, now 75. “I told Yip [co-author of the script with Fred Saidy] what bothered me about the property. It tells you that a terrible person turns black because he’s so bad, and then redeems himself and they reward him by making him white again.
“It occurred to me the story line could be made more palatable if it were done in animation. I had met Hubley. I was in the advertising business and had done some commercials with him. He was a towering genius! I made a deal with Yip to option Pinion’s for $10,000.1 underwrote the pre-production development of the property and paid Hubley to single-handedly do this remarkable storyboard. The story line became lighter and more acceptable.”
John Hubley (1914-1977) began his career in animation at age 22 at the Walt Disney Studio painting backgrounds for Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs (1937). [See PRINT, November/December 1981: "The Happy Accidents of the Hubleys."] He was an art director on Pinocchio (1940), Fantasia (1940), Dumbo (1941), and Bambi (1942) before participating in the acrimonious workers’ strike at Disney’s in 1941.

Color character sketches of Buzz, henchman and gofer for Judge Billboard Rawkins,
the story’s racial villain; a US geologist, and Howard, Judge Hawkin’s butler.
Finian’s Rainbow is an odd combination of fey fantasy and social commentary.
Walt Disney, who took the strike as a personal attack, found the opportunity to exact revenge on his renegade employees when he testified as a “friendly witness” before HUAC on October 24, 1947. He painted them bright Red. The strike, said Disney, was organized by “a Communist group trying to take over my artists and they did take them over.” Disney named names, including that of David Hilberman. Hilberman was a partner in the formation of a new animation studio, United Productions of America (UPA), staffed by dissident Disney artists, one of whom was John Hubley.
UPA’s design sensibility veered far from Disney naturalism into a modern art esthetic, and Hubley, from 1942 to 1952, was the studio’s most innovative supervising director. “In the early days,” he recalled many years later, “it was Picasso, Dufy, Matisse who influenced the drive to a direct childlike flat simplified design, rather than a Disney 18th-century watercolor. I also always had a terrific rebellion against the sweet sentimental chipmunks and bunnies idiom of animation, saying, ‘Why can’t these be human caricatures and get that same vitality in animation that still drawings have?’”
Earl Klein, an artist who worked with Hubley on storyboards and backgrounds for TV 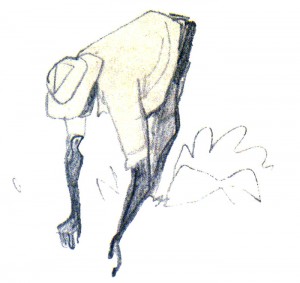 commercials in the ’50s, recalled in a 1990 interview with animation historian Michael Barrier that Hubley would ask his animators to volunteer to return to the studio in the evening. “[He] would play … a particular kind of music and have the animators go like a conga line around and around the room, listening to the music and trying to feel the rhythm and act out the emotions…. [He] said he wanted to break them away from the old established routine, the rubbery action movements that were so prevalent in those days… to influence them to be more creative in how they would see the human body in terms of animation.”
commercials in the ’50s, recalled in a 1990 interview with animation historian Michael Barrier that Hubley would ask his animators to volunteer to return to the studio in the evening. “[He] would play … a particular kind of music and have the animators go like a conga line around and around the room, listening to the music and trying to feel the rhythm and act out the emotions…. [He] said he wanted to break them away from the old established routine, the rubbery action movements that were so prevalent in those days… to influence them to be more creative in how they would see the human body in terms of animation.”

Colored pencil story sketches by Gregorio Prestopino
.
At UPA, Hubley co-created Mr. Magoo, supervised the studio’s first Academy Award-winning short, Gerald McBoing Boing (1951), and was nominated for an Oscar for his sassy stylized design and direction of Rooty Toot Toot (1952). “McBoing was a huge hit,” said Hubley. “The word started spreading that there was a new look to animation and Disney was finished!”*
Then the withering shadow of HUAC fell across UPA. “The Committee investigators dropped in and wanted the payroll book,” recalls animation director William Hurtz. “They went through names of anyone who worked there, checked some off and gave it to Columbia [UPA's film distributor], who came back and said these people have to be out of the studio or we yank the release. Most of the guys, including Hub, resigned rather than torpedo the studio. Least it could go on and some guys could have jobs. We were all on the Disney strike. I made the motion for the strike. It was a tight little club.”
“John didn’t leave voluntarily. He was kicked out!” comments Faith Hubley, John’s widow, who continues today to produce animated films at the Hubley Studio in New York City. Hubley freelanced for a nerve-racking year in Los Angeles, designing and directing animated TV commercials and, according to William Hurtz, “[making] himself scarce while the HUAC subpoenas were flying around.” Michael Shore was so concerned about Hubley’s mental state when he commissioned Hubley to create the Finian’s Rainbow storyboard in 1953, he ensconced the artist in a rented Sunset Plaza Drive house, “an isolated, beautiful setting with a 360-degree view of Los Angeles, where he could work uninterruptedly.”
“John was in love with Finian’s Rainbow,” says Faith Hubley. “It was to be the work of his life.”

Story sketches (artist unknown) of Susan the silent rushing to tell her brother, Woody,
about trouble in Rainbow Valley, the rundown tobacco plantation located near
Fort Knox, KY. Woody’s voice was provided by Frank Sinatra.
The director’s script and surviving story sketches indicate how Hubley used the medium of animation—in which the impossible is made plausible—to wrest the narrative from the confines of live-action and release it into cartoon fantasy. Preceding the title and credits, for example, Finian McLonergan distracts the leprechaun Og from guarding a crock of gold by releasing a beautiful butterfly, onto which the tiny Og leaps, “soaring off into the misty woods.” As Og gradually becomes mortal throughout the film, eventually experiencing love for two human women, he expresses this new “glow-ish, kind of perculiarish sensation” by appearing and disappearing whole and in part throughout the film, and in one charming sequence, by performing a ballet-like dance with anthropomorphic wash from a clothesline.
Leprechauns aside, most of the cast is human, traditionally the most difficult type of character to animate convincingly. But Hubley caricatures the cast, even the romantic leads (Sharon and Woody), and the exaggeration works within the film’s overall art direction. The resultant visual freedom allows for stylish treatments of potentially deadening song duets: For “Old Devil Moon,” for instance, Hubley’s script notes an “abstract sequence and Boy and Girl symbols dancing with the moon.”
Hubley once stated that his impulse with Finian‘s was to “develop the visual art even further than the UPA films had.” He felt a “need to break through and to play around with more plasticity… to get a graphic look that was totally unique to animation, that had never been
 seen before.” Rooty Toot Toot, made a couple of years before Finian‘s, demonstrates Hubley’s superbly imaginative blending of caricatured humans with impressionistic settings. Tender Game (1958), a short he designed three years after Finian‘s, shows a further development of adventurous graphic experimentation using segmented, semi-abstract figures weaving into and out of translucent backgrounds. Michael Barrier once noted that Hubley’s graphic devices “… all serve, in the end, not to explicate ideas but to delineate character… .These films are as much concerned with personality as are the best Disney films… .They have sprung from the same seed, the urge to create new life.”
seen before.” Rooty Toot Toot, made a couple of years before Finian‘s, demonstrates Hubley’s superbly imaginative blending of caricatured humans with impressionistic settings. Tender Game (1958), a short he designed three years after Finian‘s, shows a further development of adventurous graphic experimentation using segmented, semi-abstract figures weaving into and out of translucent backgrounds. Michael Barrier once noted that Hubley’s graphic devices “… all serve, in the end, not to explicate ideas but to delineate character… .These films are as much concerned with personality as are the best Disney films… .They have sprung from the same seed, the urge to create new life.”

Story sketch samples from a sequence at the colonial estate
of Judge Rawkins. The judge’s voice is that of Jim Backus.
As Hubley continued to work happily on the Finian’s storyboard, Michael Shore was having “a lot of trouble raising funds. I brought on Maurice Binder, who later became well-known for making film titles, to seek other funding sources while I concentrated on Warner Brothers.”
Binder found the newly formed Distributors Corporation of America (DCA) in New York City, headed by Fred J. Schwartz. “We were intrigued by the project,” recalls Schwartz, now 81, whose father, Abraham H. Schwartz, founded the Century Theater movie circuit and initiated the anti-trust law suit that eventually broke up studio-owned theater circuits. “We made a deal and started to put everything together. We made the deal with Yip Harburg, Saidy, and Lane, who were wonderful people. You enjoyed and loved being with them. We started to make deals with all the artists.”
“When we had the DCA money,” recalls Shore, “we started to put the soundtrack together. I was friendly with Sinatra’s accountant and with Ella Fitzgerald’s manager. Sinatra was wildly excited. It was these two great names in music together for the first time. Then we attracted all the others.”
The dialogue and song tracks were recorded in five sessions in November and December 1954 on the Samuel Goldwyn lot in Hollywood, according to Ed O’Brien, coauthor with Scott P. Sayers, Jr., of Sinatra: The Man and His Music. The Recording Artistry of Francis Albert Sinatra 1939-1992 (TSI) Press, Austin, TX, 1992). “Sinatra was at the apex of his career,” says O’Brien. “He was filming Guys and Dolls [1955], he was in The Tender Trap [1955]. It was right at the beginning of the great Sinatra period at Capitol Records. In February of 1955, he recorded ‘The Wee Small Hours,’ which many consider the greatest ballad album ever recorded.” (Ironically, that is the same date Finian’s shut down.)
Listening to the surviving sections of the nearly 40-year-old track brings the project to exuberant life. Sinatra is indeed in top form, his voice confident and vital as it combines with Nelson Riddle’s distinctive brass and string arrangements and Lyn Murray’s conducting. Sinatra’s full-out, driving version of “That Great Come and Get It Day” is particularly exhilarating. The improvised “Ad Lib Blues” duet with Louis Armstrong offers one of the few times Sinatra sang “scat.” “I was there at the recording whenTouis Armstrong did The Begat,’ recalls Burton Lane. “The shape of the number was slightly altered to make it work for what Hubley had in mind for how the number would be shot.”
“On December 2, 1954,” says O’Brien, “Sinatra recorded ‘Old Devil Moon’ with Ella Logan [star of the Broadway Finian's], full orchestra, and the Jazz All-Stars: Red Norvo, Ray Brown, Herb Ellis, Oscar Peterson, and Frank Flynn. The vocal runs eight minutes, 20 seconds. There’s a jazz riff in the middle in which Peterson challenged Norvo. It’s extemporaneous and absolutely marvelous!” By contrast, a Sinatra duet with Ella Fitzgerald on “Necessity” swings lightly with only guitar, bass, and drums for accompaniment. The change from big-band arrangements into jazz throughout the film score got full approval from John Hubley, a longtime jazz enthusiast. “I used to go out with him some evenings to listen to live jazz,” recalls Earl Klein. “We went one night to hear Prez Prado. I was very impressed with his knowledge of music.”
Faith Hubley recalls: “Sinatra wrote out the words of Tenderly’ [a song not from Finian's] for Ella, who didn’t know all of them, for a lunch-time improv with Oscar Peterson, Ray Brown, and Herb Ellis.” The extemporaneous song was recorded and used in John and Faith Hubley’s 1958 short, Tender Game, making it the only trace of the Finian’s recording sessions currently available to the general public.
A studio was opened in Hollywood to house the animation crew Hubley began hiring to create additional story sketches, color background concepts, character design models, and animation layouts. “Hub tended to drop something on an artist,” says William Hurtz, “let him explore stuff, see what he came up with. Spent a lot of money that way. Very admirable. Hub spent so much on the track that there was hardly anything left to make the picture. That is a persistent story.”
Among the Finian’s Rainbow crew were production manager Les Goldman, the painter Gregorio Prestopino, and Disney/ UPA alumni Paul Julian, Aurelius Battaglia, Ray Sherwin, and Leo Salkin. “We had more art directors on that film than I can count,” Julian told Michael Barrier in 1986. “Everybody came on hired as an art director….

Two pages from director John Hubley’s script contain spontaneous doodles in the margins -
ideas for animation bits such as a nose wiggle for Og and a belligerent walk for Finian.
Finian’s basic shape recalls that of Mr. Magoo, a character co-created by Hubley.
Hubley had put a knife in his teeth and started climbing the rigging. In order to sell the package to the kind of really upstairs talent he wanted, he promised everybody 50 per cent of whatever there was. That is not much of an oversimplification.”
Slated to animate on the film were Bill Littlejohn and Art Babbitt, one of the Disney strike leaders. Work would also be farmed out to animator/Disney striker William Tytla in New York. Anita Alvarez, the original Susan the Silent in the Broadway Finian’s, danced in a reference film shot as an aid for the animators. Maurice Binder prepared a “Leica reel,” a film of the story sketches synchronized to the soundtrack.
According to Earl Klein, Hubley’s easygoing manner made him “hard to work with because he wasn’t very disciplined.” When they worked together on TV commercials, Klein discovered that tight production schedules did not unduly trouble Hubley. “Instead of getting the storyboard out, he would be interested in something else. But then he would come in and work all night long … [and] in the morning … he had a beautiful storyboard that he had just come up with, this wild idea.” Klein feels that “of all the people I worked with in a span of 30 years, John Hubley was probably the most talented . . . most creative person I ever knew… almost a genius. He was a superior designer, also a writer. He understood music and timing beautifully. I’ve seen him direct recording sessions with musicians.”
Faith Elliott, a film/music editor and script supervisor, arrived from New York in the fall of 1954 tb work as John Hubley’s assistant. John and Faith had been friends since the war years in Los Angeles; she saw the Finian’s boards the previous year at the Algonquin Hotel in Manhattan, where Hub-ley was briefly in hiding from the Hollywood HUAC. In 1955, they were married, leading Yip Harburg to comment ruefully that “the only people who got anything out of Finian‘s was you two!”
 “There was a lot of tension in the studio,” Faith Hubley recently recalled. “Johnny had a tiny room with a piano and a sofa and an ocean of paper. He’d play the piano and get ideas and noodle around. Then there was that other room where all the people worked. The track was being recorded and edited, layouts were being made. The power situation was very, very complicated. Yip and Burton had a problem with all the jazz. Yip would complain, ‘You can’t hear the lyrics.’” Michael Shore recalls: “We had some trouble with Yip. He kept questioning Hubley’s drawings of a leprechaun. He stuck his nose in everything.” “In a sort of combination of jeers and fears,” Paul Julian recalled to Michael Barrier, “the people who were putting up the heavy loot were totally ignorant of animation, as a working process, and they kept asking to see yesterday’s dailies’ [footage developed overnight].”
“There was a lot of tension in the studio,” Faith Hubley recently recalled. “Johnny had a tiny room with a piano and a sofa and an ocean of paper. He’d play the piano and get ideas and noodle around. Then there was that other room where all the people worked. The track was being recorded and edited, layouts were being made. The power situation was very, very complicated. Yip and Burton had a problem with all the jazz. Yip would complain, ‘You can’t hear the lyrics.’” Michael Shore recalls: “We had some trouble with Yip. He kept questioning Hubley’s drawings of a leprechaun. He stuck his nose in everything.” “In a sort of combination of jeers and fears,” Paul Julian recalled to Michael Barrier, “the people who were putting up the heavy loot were totally ignorant of animation, as a working process, and they kept asking to see yesterday’s dailies’ [footage developed overnight].”
“Johnny was the director with creative control,” says Faith Hubley, “and Johnny was very strong. There was a certain amount of tension about where the picture was going—would it be too advanced for the great American public?”
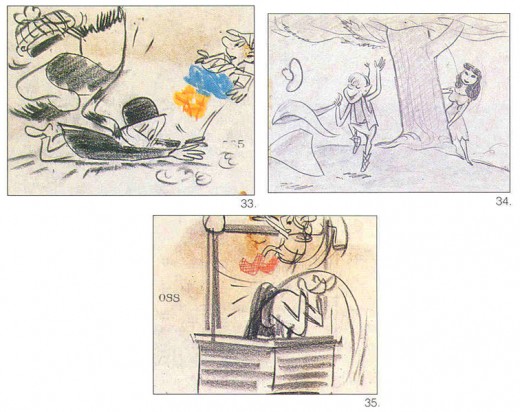
Og pursues Susan the Silent and escapes Finian, who falls down a well,
in a series of rough story sketches by John Hubley.
During this intense, anxious period, Michael Shore, the man who had conceived of the production as animation, had paid for the pre-production storyboard, and had put together elements for the spectacular soundtrack, found himself “on the outside looking in. I couldn’t even get into the office.” Angry, he went to Binder, who said, “Don’t rock the boat.” “I couldn’t bother Yip,” says Shore. “He turned his back on me.” Finally, he confronted Hubley, meeting with him “across from Schwab’s drugstore. I said, ‘I don’t want to bother anybody, but I’m being treated shabbily.’ To my surprise, John was very doctrinaire. He may have had more leftish leanings than I thought. He said, ‘I don’t give a damn. I can only think of the picture. To hell with emotions. I’ve got a job to do!’ I said he was being less than reasonable. This was my project. From day one, I had brought it to a certain point and I was going to re-introduce myself to the project. My lawyer met with DCA and we managed to shut down the production for two days while they negotiated an agreement that acceded to my involvement—a promise to return monies, an assurance of screen credit, and so on. Of course, it turned out to be a Pyrrhic victory.” Earl Klein recalls: “Hubley got so involved with the problems of Finian’s Rainbow that he began to turn a little sour and become unpredictable.”
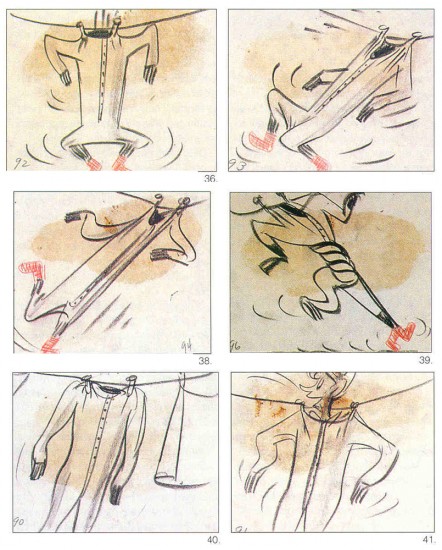
“Another pressure,” says Faith Hubley, “was the complicated representative situation. SCG [Screen Cartoonists Guild] was not IA [IATSE: International Alliance of Theatrical Stage Employees]. It had to be IA, otherwise Finian’s couldn’t play in theaters.” Bill Little-John, who was the first president of SCG, recalls he was told “I’d have to become a member of the IATSE, which had taken over Disney, UPA, MGM, Lantz, Warner’s. SCG still had contracts with the smaller studios that did TV commercials and special projects. I said the studio doesn’t select the representative of choice. It’s up to the employees. Well, that hit the fan. The backers of the film were deeply entrenched with the IATSE element; that got their backs up and created complications.”
Just how involved the IATSE was became clear when Fred J. Schwartz got a phone call from Roy Brewer, leader of the IATSE, chairman of the AFL Film Council, and chairman of the executive committee of the Motion Picture Alliance for the Preservation of American Ideals. In A Journal of the Plague Years (Atheneum, New York, 1973), author Stefan Kanfer describes Brewer as one of Hollywood’s toughest “stainless-steel” anti-Communists, a man who “no longer played the ruthless prosecutor,” preferring “the part of father-confessor, guide to the tortured and lorn.” William Hurtz recalls a command visit to Brewer’s office during the UPA purge to “listen to him lecture us on the error of our ways for being duped  by Reds, by associating with Hub and a number of the other guys.”
by Reds, by associating with Hub and a number of the other guys.”
Brewer told Schwartz he thought he was “in trouble. You’ve got a problem. Let’s meet.” The problem turned out to be John Hubley, who Brewer said “is suspect and refuses to appear before the Hollywood Committee. If he doesn’t appear and clear himself, you lose your money, you lose everything.” A shaken Schwartz met with Hubley.
“This was a very distasteful conversation for me, but I had no choice but to go through with it,” Schwartz recalls. “I said, ‘John, I got this call and I have to ask you a question. I have to swallow hard before I ask it. I want you to know I don’t believe in it, but I’m faced with a terrible situation with many individuals at risk.’ I asked, ‘Were you ever a member of the Communist party?’
“He said, ‘No. Definitely not! I will admit that like many other artists in Hollywood, I belonged to some organizations that had high-sounding names and when I found out they were fronts for the Communist party, I left them. That’s as far as I ever went.’
“I said, ‘John, we have $365,000 in the project.’ Forty years ago, that was substantial. I said, There are other people involved. Go before the Committee and clear yourself, so we can go ahead.’ He said, ‘I would be happy to, but Freddy, they’re going to ask me to name other names, and that I won’t do!”
Upon learning of Hubley’s refusal to testify, DCA’s parent company, Century Film, and their lender, Chemical Bank, decided to drop financial support of the film. But Schwartz did not give up. He sought and found $75,000 in backing from RKO, about a third of the amount needed to finish the film. Check in hand, Schwartz again approached Century. The company still refused. “And Chemical Bank said, If your own company turned you down, we can’t lend you the money,” says Schwartz, who with great sadness instructed DCA’s West Coast representative, Milton Pickman, to close the studio.
To the filmmakers, unaware of Schwartz’s desperate month-long search for money, the closing of the studio came with shocking suddenness. “It was electric!’ recalls Faith Hubley. “They impounded everything,” says designer Paul Julian, “including my stopwatch.”
“The banks refused to put up the money and it all fell apart,” says Burton Lane. “The McCarthy era was one of the worst periods. Half of my friends acted with honor and half acted with dishonor, so I gave them up. John Hubley acted with honor.” The blacklist tarred Burton’s colleague Yip Harburg, leading to, among other things, the revoking of his passport and a 12-year gap in his employment as a lyricist for movies. Earl Klein believes that word of a Harburg/Hubley collaboration originally alerted IATSE, and Hubley’s non-cooperation with HUAC doomed the production: “. . . word got around that you weren’t supposed to touch it. It was actually a blacklist and a boycott situation…. [Hubley] was in a position where the lab technicians wouldn’t handle any of… the pencil tests or anything like that. This made it impossible for them to proceed and the project had to be dropped.”
The letdown was enormous for all the parties involved. “My heart ached when it didn’t happen,” says Michael Shore. Paul Julian calls it “tragic.” “A big disappointment,” says Burton Lane. Years later, even Sinatra’s music arranger, Nelson Riddle, commented to Ed O’Brien, “It is a tragedy what happened to Finian’s.”
“What happened to me? Trouble,” says Fred Schwartz. “I was in a terrible position. The company [DCA] went under, but I had to stay with it. I didn’t have to, but I felt it was right because we owed the bank a lot of money. While I wasn’t personally liable, the company was. The bank loaned the money in part because they believed in the venture and had confidence in me. I couldn’t walk away. So I stayed with it for six years till I paid off the bank. My partners both left their jobs. They were angry at the circumstances. One had two small children at the time. You know what that made me feel like?”
“The blacklist was that powerful,” Schwartz continues. “This is an example of what happens when you squelch talent. Which is directly against everything we stand for, such as freedom of speech. This could have been a classic that would live forever.”
“The blacklist should never happen again. It certainly affected the history of animation,” asserts Faith Hubley. “If Finian’s had been finished, we’d have seen wonderful animated films of substance and content.”
HUAC eventually caught up with John Hubley; he testified for two hours and ten minutes on July 5,1956, but refused to name names, invoking his Constitutional privilege under the First and Fifth Amendments. By that time, however, HUAC and the blacklist’s power were fading; the Hubleys moved to New York, and over the years produced a series of personal animated shorts, which eventually garnered three Oscars, among other awards. “It was sad for me that Finian’s was never finished,” says Faith Hubley, “but it enabled a number of us to grow up and become strong, mature people who made all those good movies. If John had had a career doing Hollywood features, he would never have become an independent.”
Rights to the animated Finian’s and the shards of the aborted production went to a New York company, Transfilm Productions. Ironically, David Hilberman, whose name Walt Disney had put before HUAC in 1947, was hired by Transfilm, as he recently explained in a letter, to “look into how much of the picture was completed and how much time it would take to finish it.” Hilberman had been directing films in “self-imposed exile in England” after his New York studio, Tempo, was blacklisted and closed in late 1953. Consequently, he says he “was not aware of what happened in the industry…. I don’t recall any discussion about who [would work on the project] and where the project would be completed. I see now I should have checked with John Hubley, but I guess I thought that might be awkward— I am very disturbed that the Hubley production was stopped by HUAC/Brewer/black-list. Had I known, I wouldn’t have touched the assignment with a 10-foot pole!” In any case, Transfilm did not pursue the project further.
Some years after the Finian’s Rainbow debacle, entrepreneur Michael Shore approached Fred Schwartz about an animated production of Don Quixote to be storyboarded by none other than Picasso. But that’s another story.
Acknowledgment: Besides the individuals mentioned in his article, the author would like to thank the following for their help and cooperation: Michael Sporn, David Hilberman, Ernie Har-burg.Jean Gordon, Jim Logan, Nick Markovich, Brian Mainolfi, Camille Dee, Mayann Chach, Adrienne Tytla, and Amanda Deitsch (Sotheby’s, New York).
Animation Artifacts &Bill Peckmann &Disney &Models 16 Feb 2010 09:40 am
Donald Models – 2
- Last week we had the Donald Models. Actually that was the second edition of Donald models, I’ve posted. The other was a while back – back in July 2009, there was the lecture notes written of the after-hours class held in the ’30s.
As I stated, last week, this post is dedicated to model sheets of Donald that are tied to specific films he was in. I love them all. They come from several periods of Disney shorts and Donalds. The first is from my favorite period for Donald, and I’m sorry he had to change from this guy; I love him. But I also love the Mickey of that period – 1931-32.
In the end we get into the TV Donald – but not too much.
Anyway, enough gab.
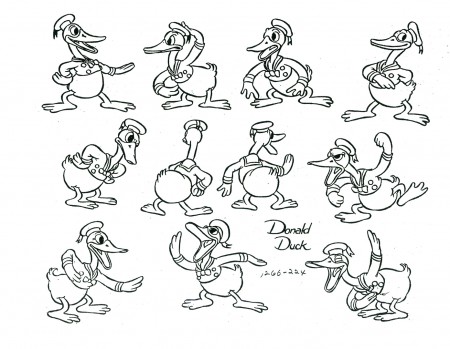
Love this character.

Hawaiian Holiday – Sept 24, 1937

Donald’s Ostrich – Dec 10, 1937

Master of the Hounds
retitled The Fox Hunt – July 29 1938
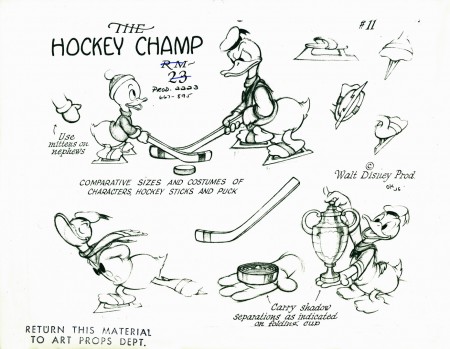
The Hockey Champ – Apr 28, 1939
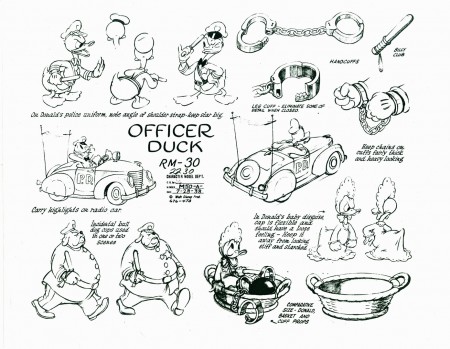
Officer Duck – October 10, 1939

Donald’s Dog Laundry – April 5 1940
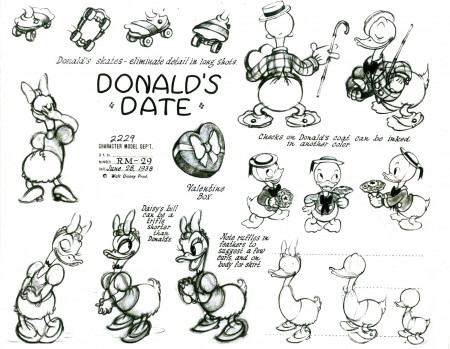
Donald’s Date
retitled Mr. Duck Steps Out – June 7 1940
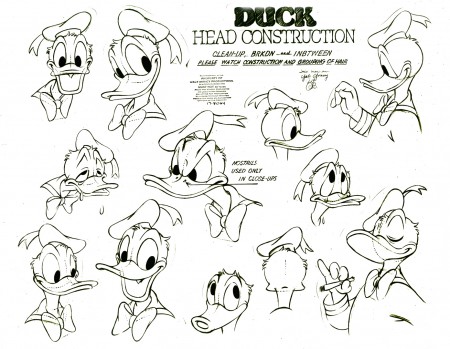
Just heads. This is getting to be late-period Donald.

Here we have one from Steel and America (1964)
an Industrial done for the U.S.Steel Corporation.
Many thanks to the gracious Bill Peckmann for the loan of this material to post. His collection of model sheets is amazing.
Daily post &Norshtein 03 Feb 2010 09:02 am
Dumbing down Oscar/Norshtein visit
- I thought I’d comment on the Oscar nominations.
The list of 10 Best Picture nominees creates some pathetic choices. The Blindside and District Nine should not be nominated for the Best Picture. It diminishes the category and demeans the other nominees. I’m sure Up got in there because of the increase to 10 nominees, but I’d gladly sacrifice that to give a little dignity to the award. The Messenger was better than either of those two films (and better than Avatar as well) yet it was left out in the cold.
They did this once before, in 1939, when every one of those 10 nominees deserved to be there. This year it was tough just picking 5 films to be nominated.
I’m glad Tomm Moore’s The Secret of the Kells got nominated, though I don’t think it was particularly good. However, it would have been a total sham if Cloudy With A Chance of Meatballs had been honored. My preference would have been for Ponyo, which may have been the best animated feature of last year’s crop.
 (By the way, there’s another chance to see the Secret of the Kells in NY. Tomm Moore will be in attendance for a Q&A. It’s playing Sat Feb 27 at the CANTOR FILM CENTER – 36 East 8th Street – at 1pm. Go here for tickets in advance. )
(By the way, there’s another chance to see the Secret of the Kells in NY. Tomm Moore will be in attendance for a Q&A. It’s playing Sat Feb 27 at the CANTOR FILM CENTER – 36 East 8th Street – at 1pm. Go here for tickets in advance. )
It’s also sad that Runaway wasn’t nominated for Best Animated Short. It’s better than most of those nominated, even though I’m not a fan of any of the shorts in the running. There were a bad crop of films shown this year, and I would have had a hard time if I had to select any of them.
I have to say, watching Logorama, which ended with a devastating earthquake, so soon after the Haitian disaster was difficult. This wasn’t the fault of the filmmakers, just the circumstances that were happening in the real world. It took something away from the film, for me.

Yurij Norshtein is visiting the two coasts.
He’ll be in San Franciso this Sunday, Feb. 7h, showing his films and talking at the Balboa Theater (3630 Balboa Street, San Francisco, CA). Tickets are $25. The event will be a fundraiser to support Yuri Norshtein’s animation studio in Moscow.
He’ll be in Olympia, Washington on Wednesday, February 10th at the Evergreen State College (Communications Building, Recital Hall in Olympia Washington.) Ticket prices are $10 regular admission, $8 seniors, $5 students.
He’ll be in LA this Friday at the USC School of Cinematic Arts (the Norris Cinema Theatre/Frank Sinatra Hall.) The admission is free and begins at 7:00pm. Friday, February 5th, 2010. Igor Kovalyev (Milch, The Rugrats, Duckman) will lead the conversation with him.
And, finally, he’ll be in New York on Monday, February 15 at the School of Visual Arts Theater (333 W. 23rd Street, between 8th/9th Ave.) This event is free to ASIFA East members (and anyone else, too.) Interesting enough, none of those who put together the NY edition of this show have any idea whether Norshtein will be screening films or just doing a Q&A. It’s up to him (and I’m pretty confident his films WILL be screened – since he doesn’t speak English, making a lengthy talk impossible.)
This is one of the great world leaders of animation, people. ATTEND ATTEND ATTEND and Stop being so lazy.
Articles on Animation &Independent Animation 21 Jan 2010 08:29 am
Len Lye
- Len Lye, one of the original experimental animators, has rarely gotten the acclaim from the animation community that he has certainly deserved. Rarely is his name mentioned in animation books or articles. As a matter of fact, in more than 50 years of reading about animation, I can only remember two significant magazine articles about the man and his work that appeared in animation magazines. (If you really go looking you’ll find a lot written in art publications – not animation mags.)
Here, I’m posting one fof those two that I think is a significant and clear article, and I hope it will give the man another five minutes of your attention. The article was written by Joseph Kennedy for the February 1977 issue of Millimeter Magazine.
by Joseph Kennedy
 Len Lye‘s Greenwich Village loft is an airy workshop, filled with the tools of the artist’s trade: machine saws, diagrams, models of projected works, and several silvery kinetic pieces glistening in the summer afternoon’s light. Len Lye himself is the Renaissance Man of the avant-garde, his prolific skills having manifested with equal success in diverse media: sketches and paintings, eel animation, paint of film, live-action films, essays and kinetic sculpture. Always the innovator, he has never bound himself to one mode of expression, choosing instead that which best suits his creative need.
Len Lye‘s Greenwich Village loft is an airy workshop, filled with the tools of the artist’s trade: machine saws, diagrams, models of projected works, and several silvery kinetic pieces glistening in the summer afternoon’s light. Len Lye himself is the Renaissance Man of the avant-garde, his prolific skills having manifested with equal success in diverse media: sketches and paintings, eel animation, paint of film, live-action films, essays and kinetic sculpture. Always the innovator, he has never bound himself to one mode of expression, choosing instead that which best suits his creative need.
For more than 50 of his 75 years he has pursued his quest of motion composition. As a teenager in Wellington, New Zealand, he had his first glimpse of the potential of this art form while delivering newspapers at sunrise. His attention was caught by the movement of clouds and he began to ponder creating artificial clouds to achieve that same quality of motion. “I thought then and there, ‘Why clouds? Why not try to compose motion yourself? — compose motion!”
After this “revelation”, he found the idea was not so easy to implement. “I tried to control motion, and I nearly broke my back. Christ, how do you? So I worked out shafts and handles that could be turned and stuck through shafts so the turning shaft could turn the particular stuff you’d stuck to it; and it was a crazy kind of attempt to control motion and compose it. I was having a ball nevertheless.”
Hoping to learn more about film, Lye moved to Australia in 1922, because New Zealand had no cinematic equipment. He worked at a Sydney studio that made animated advertising shorts. “I learned animation in Sydney, not too much because I was doing storyboards. But I took the job just to be around where people were handling film, just to see.”
 Here he chanced upon the concept of “cameraless animation”: “I didn’t invent scratching on film. I saw some guys that had made some marks on it and I rather liked the way they went (through the projector) wiggling like that, you see. I scratched a few feet of film myself, so I kept that in the back of my mind. And then I saw something like it again from a German film crowd. I think it was also some kind of scratching that they did on film. I kept that in mind too.”
Here he chanced upon the concept of “cameraless animation”: “I didn’t invent scratching on film. I saw some guys that had made some marks on it and I rather liked the way they went (through the projector) wiggling like that, you see. I scratched a few feet of film myself, so I kept that in the back of my mind. And then I saw something like it again from a German film crowd. I think it was also some kind of scratching that they did on film. I kept that in mind too.”
These experiments inspired him to adapt his own kinetic works to cinematic technique: “I suddenly realized that films had cuts and sequences. Editors can chop it where they want to. So, instead of having handles and shafts to control motion, I could just swing (objects) on a string or hold them in a black velvet glove against black velvet or whatever; you could really control and make things happen in terms of sequential motion.”
The Russian Revolution had at first created an amazingly fertile environment for the arts, and for the first time film was being considered from an artistic rather than a commercial viewpoint. Later came barbaric suppression. Lye originally planned to travel to Russia, where he hoped to get a job with the Meyerhold Theatre. He worked his passage from Sydney to London on the White Star liner EURIPEDES as a stoker, arriving in 1926. Some fortunate events enabled him to remain in London to work on his first film, TUSALA VA. “I got all sorts of fabulous help that nobody would get now. For example, as a kind of caretaker, I got a rent free barge to work on, plus the use of part of a studio to which the barge was moored on the Thames. I got a promise from the first film society in the world (London Film Society) that they would pay for the photography. And so I settled down for two years worth of animation drawings.”
One of Lye’s early stylistic influences was primitive African and South Seas tribal art. “When I first came to London I didn’t quite know what sort of imagery would carry my figures of motion. I had lived in Australia and often wondered what on earth an Aussie ‘aboe witchitty grub’ dance looked like. To get the spirit of the imagery I also imagined I was myself an Australian aboriginal who was making this animated ritual dance film.” The articulated grublike forms in TUSALA VA are reminiscent of designs on aboriginal shields, but they are dynamic moving forms. The animation was painstakingly tedious. “These goddam grubs were animated sideways, like cogs in a bicycle chain. Each cog had to be animated separately. And there were about 20 of these bloody cog-links, they all had to be animated. Why the hell I picked on that I don’t know. Well, I just plodded on, about 16 hours a day; it turned out to be both the slowest motion and the slowest animation on God’s earth!”
TUSALA VA was received rather coolly after its 1928 premiere. “Except for the art critic Rogar Fry, there was just a big silence, a complete and utter silence.” Lye found himself without the means or the support to produce another film by eel animation, and he began to consider animating without a camera, recalling his Australian experiences. “I had already used up all my goodwill stuff with the Film Society. I didn’t have much spare cash and I used to go out to some friends in Baling Studios, London, and hang around — anything to get a job in films. I used to get the old n.g. sound takes, that is, clear film with just a skinny track on one side. I would then scratch and paint and mess around with these bits of film. I would join them together and take them up the GPO Film Unit where I had some friends and run it. All this was done under the counter, you know, on lunch hours.
“I hit some marvelous effects (with) wet paint on a strip of clear film; for instance, you take an ordinary fine tooth comb and just wriggle it as you go down the length of film in the wet paint and it makes a lot of striated wavy lines. So you run it. With all these fancy abstract designs going on, the film had a very peculiar abstract quality. I was very taken by it, but didn’t have much chance of developing it.”
With the help of a composer named Jack Ellit whom Lye had met in Australia (“he was the only fellow there of the whole lot of people I knew who had any understanding of contemporary art”), he ran his film to a catchy recording of a Cuban beguine. He presented it to John Grierson and Alberto Cavalcanti at the British Government’s Post Office Film Unit. He suggested they add some slogans to the end of it. Then, with the help of Ellit, he synchronized his painted film and turned it into a public service film; and so COLOUR BOX was released in 1935, informing delightful audiences about new low parcel post rates. “A Utopian bit of public service,” thinks Lye.
 The success of COLOUR BOX resulted in subsequent films for the GPO: RAINBOW DANCE (1936), TRADE TATTOO (1937), and MUSICAL POSTER ttl (1939); as well as several advertising films: KALEIDOSCOPE (1935), for Churchman’s Cigarettes and COLOUR FLIGHT (1939) for Imperial Airways. All these films have in common the abstract “cameraless” technique used in COLOUR BOA’as well as an infectious synchronized score taken from classic jazz and Latin recordings.
The success of COLOUR BOX resulted in subsequent films for the GPO: RAINBOW DANCE (1936), TRADE TATTOO (1937), and MUSICAL POSTER ttl (1939); as well as several advertising films: KALEIDOSCOPE (1935), for Churchman’s Cigarettes and COLOUR FLIGHT (1939) for Imperial Airways. All these films have in common the abstract “cameraless” technique used in COLOUR BOA’as well as an infectious synchronized score taken from classic jazz and Latin recordings.
TRADE TATTOO is Lye’s most ambitious film (“That one’s got to be the most complex film ANYBODY’S ever done”). Lasting but six minutes on screen, it employs some of the most sophisticated editing, montage and processing effects yet seen. Using black-and-white footage from GPO documentaries, Lye combines stencilled patterns, titles and animated effects to form a brilliant montage. Each of the four layers of images that make up the final print had to be exposed three times via the old 3-color Technicolor process, requiring a total of 12 separate processes to arrive at the final color print (“the lab went crazy”). In addition, the footage was tightly edited, employing jump cuts and color reversal to synchronize with the highly percussive Rhumba and Conga beat of the score; once again, Lye was assisted by Jack Ellilt as music director. As one can imagine, the total effect is startling. Even today, some 40 years after its conception, its avant-garde approach still seems fresh and contemporary, capable of rousing an audience to cheers.
 Len Lye turned his hand to live action films, directing several shorts for the GPO. In 1944, he was invited to America to direct films for the “March of Time”. Although his 1958 short abstract film FREE RADICALS won the Silver Medal at the Brussels World’s Fair, Lye began devoting more of his time to kinetic sculpture. “My type of film, which is a short film, might take me eight months; and it’s very definitely fine art, not folk art in any shape or form. I take eight months to make five minute’s worth of film. Nobody is going to pay me for any of those eight months. And in any case, it’s a pain in the neck to have a five-minute film. How’s it going to be laced up and tied in with the rest of the program? People go to a movie house to see a program of at least ninety minutes, and they couldn’t care less whether they miss a five-minute fine art job. So my films were a complete anomaly.”
Len Lye turned his hand to live action films, directing several shorts for the GPO. In 1944, he was invited to America to direct films for the “March of Time”. Although his 1958 short abstract film FREE RADICALS won the Silver Medal at the Brussels World’s Fair, Lye began devoting more of his time to kinetic sculpture. “My type of film, which is a short film, might take me eight months; and it’s very definitely fine art, not folk art in any shape or form. I take eight months to make five minute’s worth of film. Nobody is going to pay me for any of those eight months. And in any case, it’s a pain in the neck to have a five-minute film. How’s it going to be laced up and tied in with the rest of the program? People go to a movie house to see a program of at least ninety minutes, and they couldn’t care less whether they miss a five-minute fine art job. So my films were a complete anomaly.”
Nevertheless, Len Lye is still deeply involved in the creation of a new iconography, encompassing all the arts — a new understanding of the relationship mankind, myth, and creativity have in the scheme of life. “I think Art is the only way you can isolate the creative essence of humanity. This essence, like happiness, is individuality. Civilizations and religions may fall down the drain, but their arts remain. It takes the avant-garde to best symbolize the vitality of creativity. There are a lot of great parallels between great, or everlastingly evocative, happiness and great art. This relationship is mainly about value — human value, and it can teach us how to get the most out of ourselves, and life, that we can.”
Photos:
1. Len Lye and a slide from Tusalava (1928) (Photo by John Canemaker)
2. Trade Tatoo by Len Lye (Courtesy of Cecile Starr)
3. Rainbow Dance by Len Lye (Courtesy of Cecile Starr)
4. Joseph Kennedy (L) interviews Len Lye (photo by John Canemaker)
Joseph Kennedy is a New York City schoolteacher and a freelance writer. He has taught film history at Regis High School and he reviews films for Film news.
The magazine gave the above short bio about Mr. Kennedy in the Contributors column. Joe is a friend, and I am aware of how limited this makes his work seem (given that it was written in 1977.) He subsequently became a public relations executive and now has his own corporate communications practice; he worked with John Canemaker and Peggy Stern on The Moon and the Son and Chuck Jones: Memories of Childhood.
There is more information about Len Lye at several websites.
The Govett-Brewster gallery gives some good information about the man and his work.
Senses of Cinema offers an extensive bibliography of books and articles about the man.
Several of his film are available on YouTube (of course) in slightly degenerated versions:
Color Box
Swinging the Lambeth Walk
Particles in Space
Kaleidescope