About six weeks ago, I was contacted by Peter Hale in the UK about a “strip book” of Peter Pan that was published in England to tie into the original release of the movie. Peter sent me some beautiful scans of the artwork in the book, and I posted it (here.)
Mr. Hale promised a second book that was also published at the time.
It turns out he has done some extensive research into the subject of the books in conjunction with the Disney film. This week, I received a complete breakdown of all the “Pan” books that were published in the UK, and the scans for another book. I’ve decided that I really have to post what Peter has written; it’s that extensive. I’ll follow up with another post of the books scanned.
Many thanks to Peter Hale for sharing this fine work with the “Splog” and its readers.
The rest of this post is over to Peter Hale who writes:
_________________
 My (superficial) research into the Disney-illustrated books of Peter Pan published
My (superficial) research into the Disney-illustrated books of Peter Pan published
in the UK in 1953 has wandered off on several tangents.
Firstly a rough chronology of the development of the original book, and the Disney
film:
1902 – Barrie’s fantasy novel (for adults) The Little White Bird includes a sequence that
features Peter Pan, a 7-day-old baby who flies away from home so that he will never
grow up, and, after learning that he is not a bird, and therefore can’t fly, is
adopted by the faries in Kensington Gardens.
1904 – Barrie expands the idea of Peter Pan into a play, to great success.
1905 – The chapters from The Little White Bird that feature Peter Pan are republished for
children as Peter Pan in Kensington Gardens by his publishers, Hodder & Stoughton,
to cash in on the play’s popularity.
1911 – Because of the demand for Peter Pan products, Barrie publishes a novel based on the
play. He adds a coda wherein Peter promises to return each spring to take Wendy back
to Neverland to do the Spring Cleaning. But he starts to miss years, until he has
forgotten her altogether. Wendy grows up and has a daughter of her own. One day
Peter returns for her and is distressed to find that she is too old to fly away. But
he soon meets her daughter Jane and so takes her to Neverland, and when she grows
old, her daughter Margaret will take over – because he does need a mother.
1915 – Hodder & Stoughton publish an abridged version of Peter Pan for younger children,
written by May Byron with Barrie’s approval. They title it Peter Pan & Wendy.
1921 – A version of May Byron’s adaptation “retold for Little People” is published, with
illustrations by Mabel Lucie Attwell at Barrie’s request. Her drawings of babylike
characters presumably matched Barrie’s vision.
1929 – Barrie donates all the rights to ‘Peter Pan’ to the Great Ormond Street Hospital for
Children.
1935 – Walt Disney plans to follow Snow White with Peter Pan, but has difficulty securing
screen rights from Great Ormond St Hospital.
1939 – Having finally secured rights to make an animated film version, the Disney studios
schedule Peter Pan to follow Bambi and Pinocchio.
1941 – The entry of the US into WWII forces Disney to postpone productions.
1947 – The Disney Studios put Peter Pan back into production.
1953 – February 5th: Walt Disney’s Peter Pan premieres at the Roxy Theater, New York.
1953 – April 16th: Walt Disney’s Peter Pan has its UK premiere at the Leicester Square
Theatre, London.
1953 – May: Walt Disney’s Peter Pan is shown at the 6th Cannes Festival.
1953 – July 27th: Walt Disney’s Peter Pan goes on general release in the UK.]
During the 30s Mabel Lucie Attwell became famous for her drawings of cute children.

Through the 40s her characters became ever more chubby, stunted and stylised, but in 1915 she was still starting out as an illustrator.
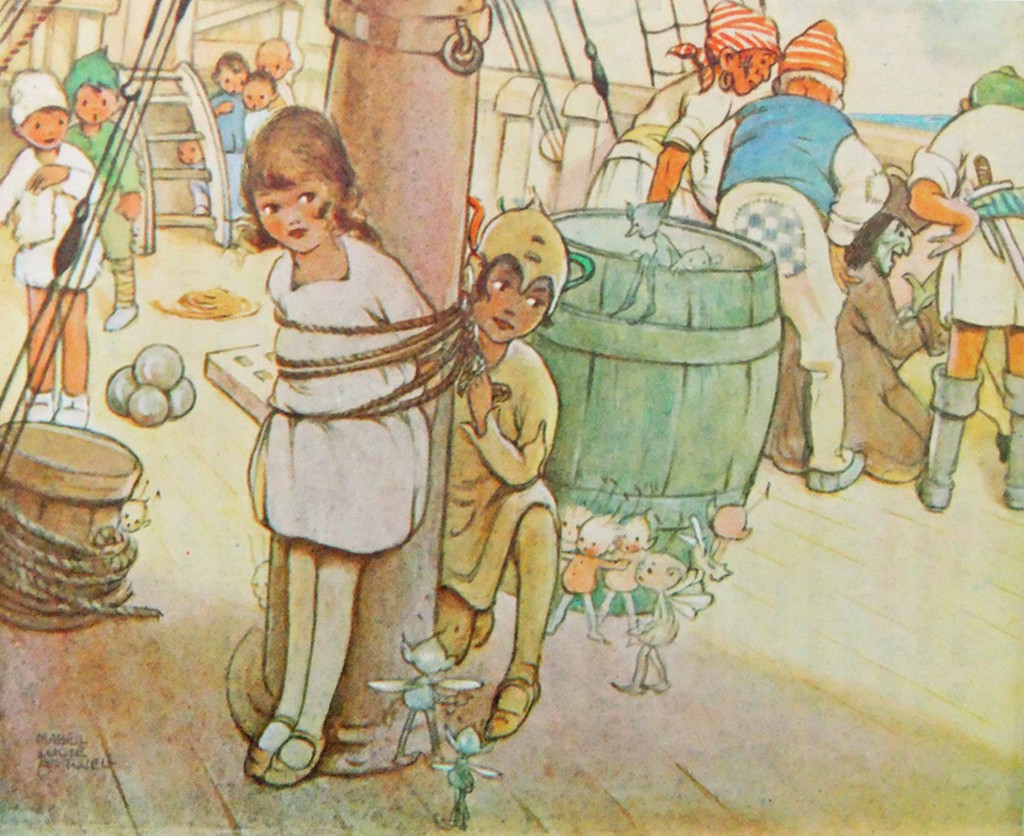

Here is her version of Peter freeing Wendy from the mast.
The illustrations she did then became almost as much part of the May Byron version of “Peter Pan and Wendy” as Tenniel’s were part of “Alice”, and it was still being published in 1980. A reprint of the 1921 edition was published in 2011.
Which brings us to the versions of Peter Pan published in the UK in 1953.
Jacqueline Rose, in her book “The Case of Peter Pan”, lists the following six books published in the UK that year:
- Barrie, J. M. Peter Pan in Kensington Gardens, illustrated by Arthur Rackham, ‘Peter Pan Books’ (from 9 years) (London: Hodder and Stoughton, I953)
- Bedford, Annie N. Disney’s Peter Pan and Wendy, ‘Peter Pan Books’ (London: Hodder and Stoughton, I953)
- Byron, May. Peter Pan in Kensington Gardens, illustrated by Arthur Rackham, ‘Peter Pan Books’ (for 6 to 8 year olds) (London: Hodder and Stoughton, I953)
- Byron, May. The Walt Disney Illustrated Peter Pan and Wendy, ‘Peter Pan Books’ (for 8 to 9 year olds) (Leicester: Brockhampton Press, I953)
- Pearl, Irene. Walt Disney’s Peter Pan, retold from the original story by J. M. Barrie, ‘Peter Pan Books’ (for 3 to 6 year olds) (Leicester: Brockhampton Press, I953)
- Winn, Alison. Walt Disney’s Peter Pan, retold from the original story by J. M. Barrie ‘Peter Pan Books’ (for 6 to 8 year olds) (Leicester: Brockhampton Press, I953)
as opposed to just one in 1952:
- Byron, May. Peter Pan, retold for the nursery, illustrated by Mabel Lucie Attwell, ‘Peter Pan Books’ for 3 to 6 year olds) (Leicester: Brockhampton Press, I952)
Two of these are versions of the Peter Pan in Kensington Gardens ‘origin’ story, which Disney had decided not to include in the film.
The remaining 4 are all “Illustrated by Walt Disney”. The Irene Pearl version is the strip book already posted, and scans of the May Byron book and the Alison Winn “Little Book” will follow. These all follow the Barrie novel rather than the Disney film, although with different simplifications and omissions.
The Annie N. Bedford book is one I have not been able to trace – she is the American author who wrote the Golden Books version of the Disney film, so this could be a UK publication of that book. It is given as published by Hodder & Stoughton, Barrie’s original publisher. The back cover of the Brockhampton ‘Little Book’ lists a different Hodder & Stoughton book.
“J. M. Barrie’s original Peter Pan and Wendy for older Boys and Girls, with illustrations by Walt Disney”. I have not been able to trace a copy of either book. These two books represent the two ends of the spectrum:
Barrie’s original text and the story of the film.
Finally there is the complication of Dean & Son’s Walt Disney’s Peter Pan, from the motion picture, a book of the film. This has no publication date. The illustrations are given as copyright Walt Disney 1953, but this is not a guide to the publication date, as Disney did not own the publishing rights and so the illustrations were always copyrighted to 1953, the year of the film’s release. It is probable that the Dean book was published later than 1953.
It is published ‘by arrangement with Hodder & Stoughton’, which either means it may be a reprint of the Bedford book, or just an acknowledgement that Hodder held the publication rights to Peter Pan.
In contrast I can only find one UK ‘Disney’s Alice in Wonderland‘ book that might have been published in 1951, and certainly no Carroll text with Disney illustrations.
So why so many Peter Pans? The UK’s wartime paper rationing ended in 1950 so that would not be an issue.
Was it because Disney did not have the publishing rights, so this collaboration was necessary to promote the film?
Was it just, as I’d thought previously, that the British might object to tampering with the story? Or was Disney just trying to overcome the sort of criticism that his Alice had suffered in the UK (that it was too Americanised and not sufficiently true to the book) by linking his film to the original text?
Comparing the 3 Brockhampton books the illustrations are all different, and by different hands it would appear, but all show fidelity to the Disney style. I am assuming that these illustrations were done by British illustrators specially for the books, as where the illustrations differ from the film the artists seem to have consulted the particular text they are working with for details.
Hence the May Byron text describes the adding of a shoe as a knocker, and John’s hat as a chimney, and the illustration shows the hat, although it also shows Wendy watching the building from outside, which is quite wrong!

The illustration of the house in the Alison Winn book, which does not include those details, does not show them either, and the same is true of the Irene Pearl strip book.
The marooning of Tiger Lily is done in the book by two pirates, with Hook turning up
later.

In the
May Byron book they are named as Smee and Starkey, and the
illustration has Hook replaced by a likeness of the Disney Starkey (but with a
yellow shirt instead of pink). The strip book doesn’t name the pirates and Hook is
here replaced by Bill Jukes. The
Alison Winn version omits the marooning of Tiger Lily entirely and just has Hook turn up to attack Peter.
All three books have Wendy exhausted and Peter injured after the encounter – both
stranded on the rock unable to fly back. John’s kite collects Wendy, while Peter is
rescued by the Never bird, whose floating nest serves as a boat. The Winn ‘Little
Book’ uses a version of the shot of Peter and Wendy watching Hook and Smee from on
high, but without the pirates, truncated to appear a low rock, and with a kite added
in.
This brought me to wonder how much Disney reference they were given, and what it
consisted of. Many of the scenes are close to shots from the film. But a look at the
Dean book, which seems to be taken directly from colour stills, shows that these are
not actually shots from the movie.
Anyone who has ever tried to put together presentation scenes from the cels of an
animated film knows that there are always problems – the best pose is poorly traced,
or one character is in an ungainly inbetween position – whatever, that perfect key
image from the storyboard just isn’t there in the actual film, where, deliberately,
nothing hits a strong extreme at the same time.
Hence it appears that the lobby card stills or coloured transparencies that Disney
circulated in their press packs etc. had been specially recreated – a lead animator
had redrawn the characters from various key frames as they ought to have looked, and
these drawings had been traced and painted on cel with extra care, and combined with
a new version of the background to be photographed by a stills camera. (I presume
the composites then went up on someone’s wall!) The same thing, of course, as the
re-posing of key scenes that is typically done by a stills photographer on the set
of a live action film after it has been shot.

The illustrators appear to have had coloured stills and model sheets to work from.
Does anyone know how much reference was supplied? Walt Disney Studios had an office
in London specifically to deal with promotion, distribution, licensing artwork etc.
Did they do artwork for any of the books – or just supply references?
Lastly, the curator of the Great Ormond St. Children’s Hospital Archives has kindly
sent me these scans relating to the London Premiere of Peter Pan on 16th April 1953



It’s worth taking note that Hans Perk has recently posted the animators’ drafts from the Disney film, Peter Pan. Go here to read and/or collect them.
 We’ve seen that Tytla veered his animation style completely toward the “Method” and there is no doubt that he carried that with him even after he left the Disney studio. Unfortunately, he went to the lowest of the low and couldn’t survive any longer as an animator. He turned to direction and had to adapt his use of Stanislavsky to his directing technique.
We’ve seen that Tytla veered his animation style completely toward the “Method” and there is no doubt that he carried that with him even after he left the Disney studio. Unfortunately, he went to the lowest of the low and couldn’t survive any longer as an animator. He turned to direction and had to adapt his use of Stanislavsky to his directing technique.  1
________________________
1
________________________