Articles on Animation &Hubley &Independent Animation 29 Jun 2010 07:46 am
Traditional Animation Transformed
- Mike Barrier wrote an excellent article on the Hubleys for the 1977 Millimeter Magazine animation issue. Short and concise, it really put their careers and their work into fine focus. The magazine was released in February 1977, just prior to John’s death, February 27th of that year.
With Mike’s consent, and my grateful thanks, I’m posting it here. (I haven’t given enough attention to John and Faith lately.)
Traditional Animation
Transformed
by Mike Barrier
For more than 20 years, John and Faith Hubley have been hacking an idiosyncratic path through the jungle of post-war animation. Temperamentally — one might almost say ideologically — they are avant-garde, but they have little in common with the frauds and bores who have appropriated that label for themselves; you will not find their names in the index for the new book Experimental Animation. They have firmly and frequently turned their backs on the animation tradition rooted in Walt Disney’s cartoons — yet their films are linked to that tradition in various and subtle ways. The Hubleys have made films for television, but of all the people who have worked in that medium, they would seem the least likely to work on an animated special that was in any way conventional. However, they have now turned their hands to a TV special based on a comic strip.
Neither the comic strip nor the Hubley’s method of transferring it to the small screen are conventional, however. The comic strip is “Doonesbury,” and the Hubleys are making the special in close collaboration with Garry Trudeau, the strip’s artist-author. The storyboards are a mixture of Hubley and Trudeau drawings, and Hubley says that he, Faith and Trudeau cast votes of equal weight when decisions are made on the story. The special will be on NBC, probably in either the spring or early summer of 1977.
Trudeau and the Hubleys are not strangers; they met in 1968, when Trudeau was a student at Yale and the Hubleys were teaching their first classes in a course called “The Visualization of Abstract Concepts.” Animation courses are common now on U.S. campuses, but the Hubleys’ course is markedly different from most others. The students are not taught how to animate; instead, they are taught to think in certain ways. In effect, they are encouraged to devise animatable symbols for abstract ideas. The ideas generated in the course are converted into animated films later by the students as well as the Hubleys and their staff. Voyage to Next — in which nationalism is represented by boxes filled with people, floating aimlessly on the stream of history – went through the Yales class process as did Cockaboody and EVERYBODY RIDES THE CAROUSEL, a feature-length film, based on the writings of Erik Erikson, that was shown last fall on CBS.
Despite its origins in Yale’s rarefied atmosphere, the “Doonesbury” special will be aimed at a larger audience than the Hubleys have ever sought before (except in the TV commercials they used to make). It is, unavoidably, a highly commercial project, and so, filled with pitfalls for two filmmakers who have steadfastly turned their backs on mass taste.
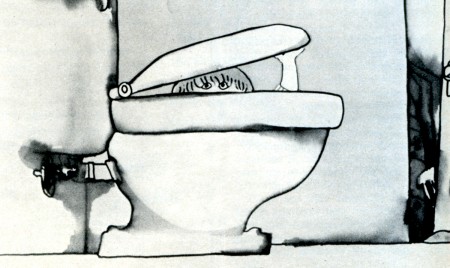
Cockaboody, a tender and sensitive commentary on childhood.
John Hubley ventured into the world of big money and high-powered entertainment in August 1975, when he became the director of an animated version of WATERSHIP DOWN. He was discharged from that job a year later, after sharp disagreements with the producer, Martin Rosen, over creative and production control of the film. Hubley had spent half of the 12 months he worked on the film in England, and half in the U.S., working with both American and British crews. (Bill Littlejohn and Phil Duncan were among his American animators.) Hubley’s comments about the break with Rosen are guarded, because he has filed a suit against Rosen for breach of contract; but it seems plain that Rosen wanted a more violent and emotional film than Hubley was prepared to give him.
Throughout their long collaboration, the Hubleys seem to have been happiest when they could work in an atmosphere entirely free of commercial considerations. Since they began working as a team in 1956, their work has fallen, roughly, in three categories: purely commercial films, like TV spots; sponsored films, which come equipped with fixed budgets but considerable creative leeway; and their purely personal work — Moonbird, Tender Game — which they financed with their earnings from the other kinds of films.
In all three types of films, the Hubleys have employed a dazzling variety of techniques, ranging from traditional line animation to the animation of blocks of color to the animation of cutouts. Two elements have been constant. All of their films reflect the influence of modern art — or, to be frank about it, modern art as it has been adapted and domesticated by commercial artists and designers. More important than the graphic style itself is the use to which the Hubleys have put it (and this is the second constant in their work): abolishing the traditional distinction between characters and backgrounds.
In a typical Hollywood cartoon of the ’30s or ’40s, the characters move against the backgrounds like actors working in front stage settings. The characters are composed of lines and flat, bright colors, against settings that are realistically modeled and painted in muted colors. The characters are treated as color accents; they “read” against settings that are designed to set them off.

A still from Moonbird.
In most of the Hubleys’ films, no such boundary exists; characters and settings are cut from the same bolt. Movement alone sets them apart. This integration of characters and backgrounds — not any simple enthusiasm for modern art — was at the heart of the UPA studio’s rebellion against the Disney style in the middle ’40s. It was a layout man’s rebellion. The ultimate effect was to elevate design — the overall “look” of a film — at the expense of animation. Layout men, who had been subordinate to the animators at Disney’s, were now in the driver’s seat.
Two of UPA’s three original partners — Zack Schwartz and Dave Hilberman — had been Disney layout men, as John Hubley was. When Hilberman and Schwartz broke with Steve Bosustow (the third partner) in 1947, Hubley became a vice president of the studio, and its creative head. Hubley supervised the work of directors like Robert Cannon and Pete Burness, and directed a number of films himself, most notably Rooty Toot Toot (1952). The most distinctive UPA films thus bear Hubley’s stamp, more than that of any other man.
Hubley left UPA in the early ’50s; he was a victim, like many other UPA staffers, of the witch hunts by the House Committee on Un-American Activities. He formed his own TV-commercial studio, Storyboard, and then he married Faith Elliott, who had been hired as his assistant for an aborted production of Finian’s Rainbow. Faith — who had worked in live-action films before marrying John — has been his collaborator ever since; but their films are, in some ways, extensions of the work that John Hubley did at UPA, but reflect a less commercial, more personal approach. (Faith Hubley has completed two films of her own in the last two years: W.O.W. and Second Chance.)
UPA sold itself not only as an alternative to the Disney style, but as a repudiation of it. John Hubley still talks that way on occasion, and the Hubley films sometimes become pretentious and didactic. Films like The Hole (1963) and The Hat (1964) while nice to look at, suffer from windy, enervating dialogue tracks; the lessons they offer — about international boundaries and nuclear war — are too simple to bear repetition for even a few minutes. Of Men and Demons (1970), is also a “lesson” film — this time the Hubleys are concerned about the environment — but it is much better because the villains of the piece (demons representing fire, wind and rain), are ingratiating scoundrels; the characters are stronger than the ideas they are supposed to serve.

Adventures of an *.
Here we come to a paradox in the Hubley films. The best ones — the ones in which the Hubleys’ own feelings and experiences are to the fore — have a great deal in common with the Finest cartoons in the despised Disney tradition. Some of the very best Hubley films, such as Moonbird, Windy Day, Cockaboody and the opening sections of Everybody Rides the Carousel, are tender and sensitive commentaries on childhood. The graphic devices, the quicksilver metamorphoses — as children become what they imagine themselves to be, and beasts lunge from the mouths of howling babies — all serve, in the end, not to explicate ideas but to delineate character. In other words, these films are as much concerned with personality as are the best Disney films; they are very different from the Disney films to be sure, but they have sprung from the same seed, the urge to create new life.
The best Hubley films do not spit in the face of animation’s greatest tradition. Instead, they show how that tradition could be transformed and enriched, if it were still in the hands of people who cared as much about their work as the Hubleys care about theirs.
© 1977 Mike Barrier



on 29 Jun 2010 at 10:02 am 1.Andriana Ruzic said …
thank you, michael s, thank you michael b, it will be sooooo useful for my work on the hubleys!
on 29 Jun 2010 at 5:13 pm 2.Eric Noble said …
Excellent post Mr. Sporn. Please thank Mr. Barrier for his wonderful, insightful article on two wonderful animation artists. I will have to check out their work on YouTube. It’s not the best way, but it’s the only way I can. I hope to be able to create my own personal films the way they did. I am constantly inspired by what I read on here.